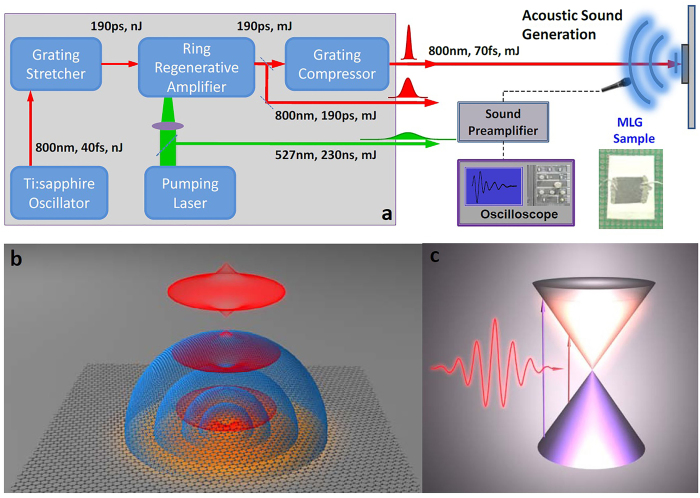
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the experimental setup and sound generation mechanism.
(a) Ultrafast laser pulses of different wavelengths, time durations, and repetition rates are irradiated onto the graphene sheet sample. (b) Ultrafast laser pulses generate a thermal gradient which leads to acoustic sound wave generation. The time interval between pulses phase-controls the sound amplitude. (c) MLG under ultrafast laser pulse excitation. The electron-phonon interaction generates thermal heat during the ultrafast (ps) relaxation process, which further produces acoustic sound at a much longer (μs) time scale. The cones are used to mimic the band structure of MLG.