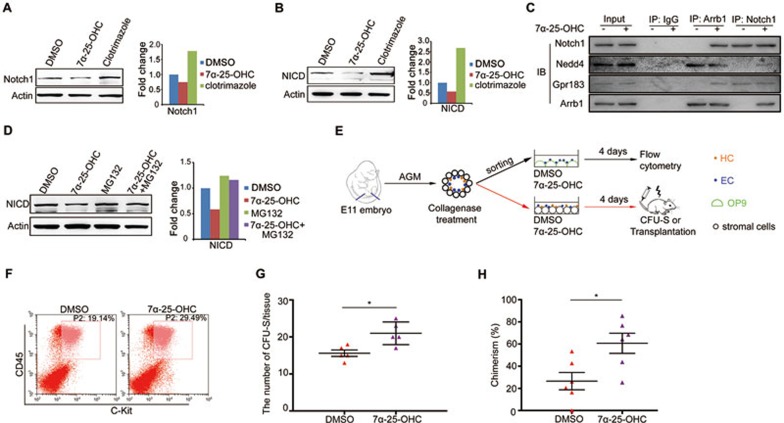
Figure 7.
Gpr183-Arrb1-Notch1 signaling cascade is conserved in mammals. (A, B) Notch1 and NICD expression in E10.5 mouse AGM cells treated with clotrimazole or 7α-25-OHC for 1 h. (C) Western blot detection of Gpr183 or Notch1 in anti-Arrb1 or anti-Notch1 IP product from E10.5 AGM cells. Equal amounts of Notch1 were used in the co-IP assay as 7a-25-OHC treatment decreases Notch1 expression and thus it is difficult to detect Notch1-precipitated proteins in the IP assay. (D) Decrease in NICD expression in 7α-25-OHC-treated E10.5 AGM cells is rescued by MG132. Right panel shows the quantification of western blot data. (E) Flowchart for isolation, culture and transplantation of mouse AGM cells. For flow cytometry, pan-ECs (CD31+CD41−CD45−Ter119−) were sorted from cell suspension obtained from E11 mouse AGMs and treated with DMSO or 7α-25-OHC for 4 days. For CFU-S or long-term transplantation assay, total E11 AGM cells were treated with DMSO or 7α-25-OHC for 4 days. (F) Flow cytometry showing an increased amount of c-Kit+CD45+ cells from 7α-25-OHC-treated E11 mouse AGM pan-ECs. (G) Quantification of results from the CFU-S assay (n = 5). (H) Donor-derived chimerism. AGM cells from actin-GFP transgenic mice were treated with DMSO or 7α-25-OHC (1 μM) for 4 days, mixed with bone marrow carrier cells, and were injected intravenously into irradiated female mice (GFP−). Three months later, bone marrow cells were collected for the analysis of GFP+ chimerism. Error bar represents SD. *P < 0.05.