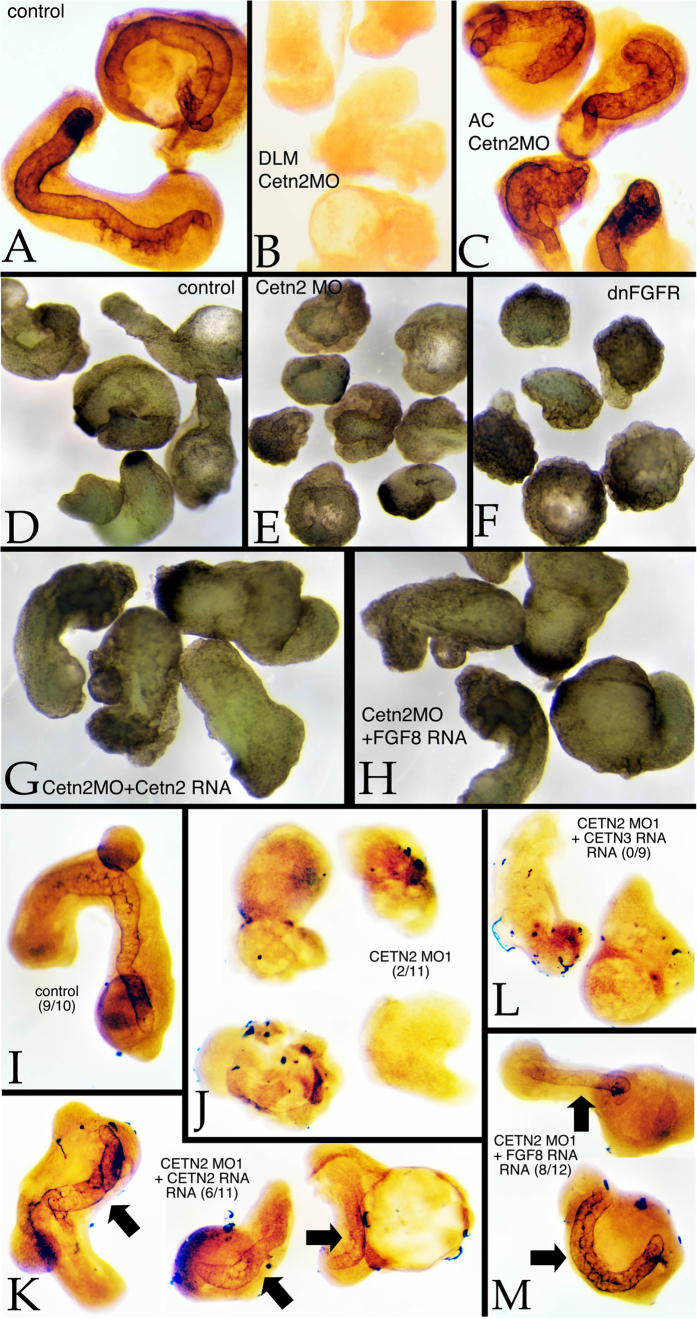
Figure 3.
Animal cap/dorsal axial mesodermal zone (AC/DAMZ) explants were prepared from experimentally manipulated embryos when control (intact) embryos had reached stage 25. In wild type explants (A) staining with the anti-keratan sulfate antibody MZ15 revealed explant elongation and notochord formation. Both were absent in wild type AC/Cetn2 morphant DAMZ explants (B). Notochord formation occurred in Cetn2 morphant AC/wild type DAMZ explants (C). A comparison of dorsal axial mesoderm explant morphology (D-H) revealed the elongation of control explants (D), this elongation phenotype was absent in Cetn2 morphant explants (E) and dominant-negative FGFR RNA injected explants (F). In Cetn2 morphant explants, the elongation phenotype was rescued by either Cetn2-GFP (G) or FGF8 (H) RNA injection (200 pgs/embryo). Morpholinos were injected at 10 ng/embryo. Staining with MZ15 revealed the presence of notochordal tissues in control (I) explants, its absence in Cetn2 morphant explants (J), and its reappearance in Cetn2 RNA (K) and FGF8 (M), but not in Cetn3 RNA (L) injected Cetn2 morphant explants - number of explants with notochord staining per total number of explants is presented in brackets in panels I-M.