Figure 1.
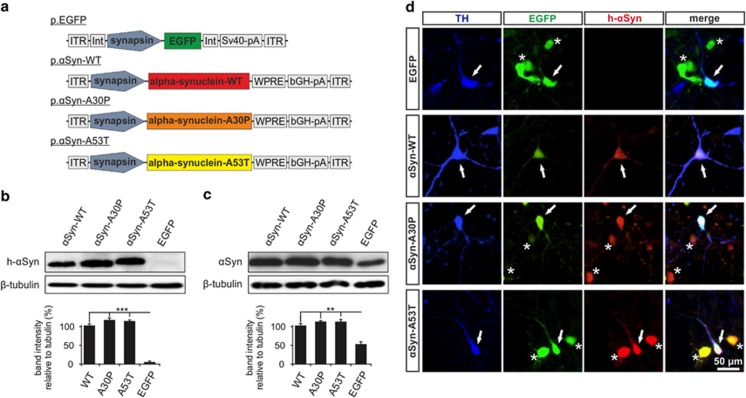
Overexpression of αSyn variants in PMN. (a) Vector maps of the plasmids used to overexpress EGFP, αSyn-WT, -A30P and -A53T. The respective transcripts are expressed under the control of a human synapsin-1 promoter. ITR: AAV-2 inverted terminal repeat. Int: intron. SV40-pA: SV40 polyadenylation site. WPRE: Woodchuck hepatitis virus posttranscriptional regulatory element. bGH-pA: bovine growth hormone polyadenylation site. (b and c) Immunoblots of whole cell protein lysates from PMN transfected with the given plasmids (cells were lysed on DIV 5). In b, an antibody specific for human αSyn (LB509, Invitrogen) was used to detect only the αSyn expressed by the plasmids. In c, total cellular αSyn levels were assessed using an antibody recognizing both human and rat αSyn (BD). At the bottom, quantifications of the band intensities normalized to β-tubulin are shown (n=3; error bars represent means±S.E.M.; **P<0.005, ***P<0.0005 according to one-way ANOVA and Dunnett's posthoc test). (d) Immunocytochemistry of PMN transfected with the plasmids given on the left side and stained against tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) to identify dopaminergic neurons and human αSyn (LB509, Invitrogen) to check for successful transfection with the respective plasmids (micrographs taken on DIV 5). EGFP is expressed by the plasmid p.EGFP that is either transfected alone or co-transfected with the αSyn-plasmids. Arrows highlight transfected dopaminergic neurons, asterisks mark transfected non-dopaminergic neurons