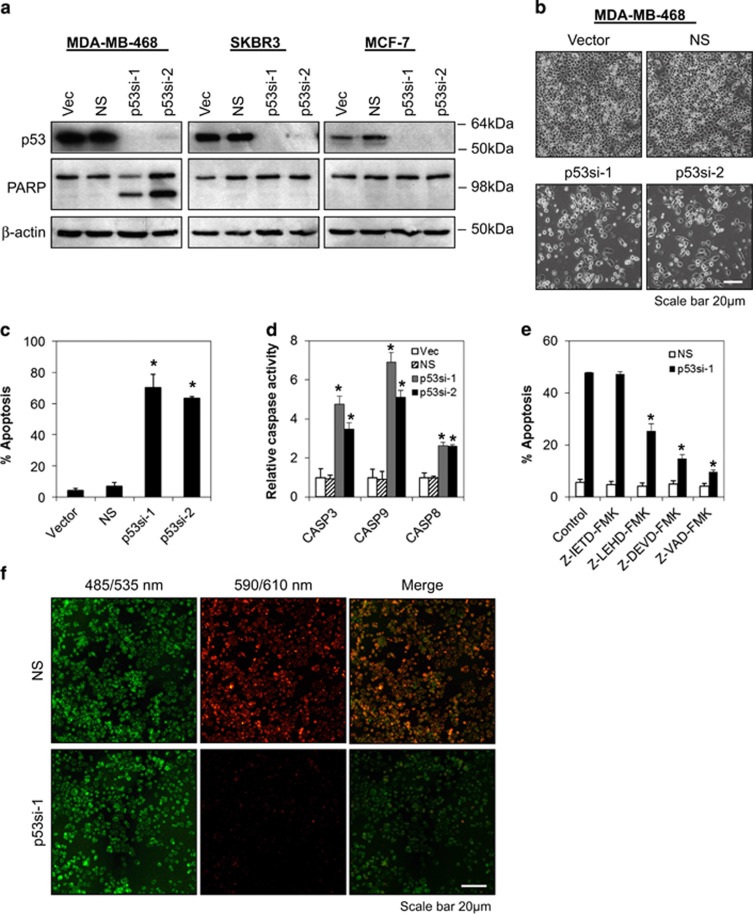
Figure 1.
Knockdown of endogenous p53-R273H contact mutant, but not R175H conformational mutant, induces mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. (a–c) Mutant p53-R273H is required for the survival of human breast cancer cells. Cells were transduced with control vector (vec), non-targeting (NS) and two different lentiviral constructs that specifically target human p53 (p53si-1 and p53si-2). Lysates were prepared for immunoblotting at 72 h after transduction. β-actin serves as a loading control. Morphological changes were observed at 96 h after lentiviral transduction by light microscopy (original magnification × 100). Apoptotic cell death was determined using annexin V/7-AAD flow cytometry at 96 h after transduction. (d) Knockdown of mutant p53 induces caspase 8, 9 and 3 activation. Caspase activities were assessed by CaspaseGlo assay at 72 h following transduction. (e) Depletion of mutant p53 in MDA-MB-468 cells induces apoptosis which requires caspase 9 and 3, but not caspase 8, activities. Caspase-dependent cell death was evaluated by annexin V/7-AAD flow cytometry in the presence or absence of 20 μM of caspase inhibitor following mutant p53-R273H knockdown. (f) Knockdown of mutant p53 in MDA-MB-468 cells induces mitochondrial membrane depolarization. Cells were stained with JC-1 at 72 h after p53 lentiviral shRNA transduction. Red color indicates the presence of JC-1 aggregates in intact mitochondria. Green color indicates JC-1 monomers in the cytoplasm. JC-1 stained cells were analyzed using epifluorescence microscopy (original magnification × 100). Bars represent mean±S.D. of three experiments. * indicates statistical significance (P<0.05) by Student's t-test