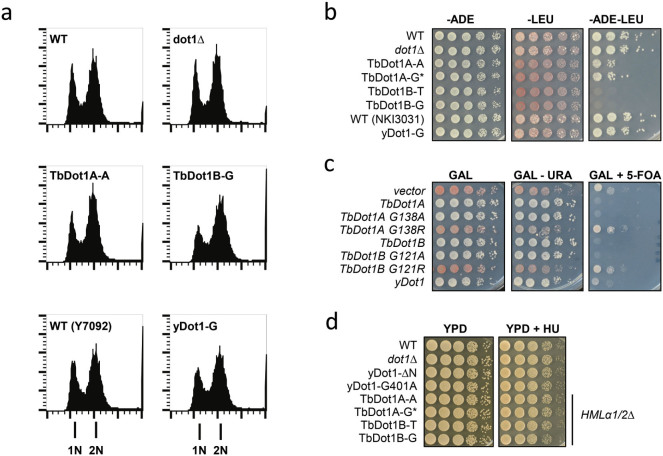
Figure 6. Expression of TbDot1A or TbDot1B in yeast affects silencing but not replication.
A) Cell cycle progression of yeast strains overexpressing yDot1, TbDot1A or TbDot1B was determined by flow cytometry (FACS) analysis of DNA content and compared to the wild-type strain NKI6061 (WT). X-axis depicts DNA signal, Y-axis depicts cell count. The promoter from which the Dot1 enzymes were expressed is indicated behind the dash: A = ADHpr, G = GPDpr, D = DOT1pr. Strain Y7092 was used as the WT control for yDot1-G. B) To test whether the altered H3K79 methylation profiles affected silencing of the silent HMLα mating locus yeast strains expressing yDot1, TbDot1A or TbDot1B in a MATa ADE2 + leu2Δ background were mated with a WT strain with a MATα ade2Δ LEU2 + background (BY4726). Loss of HMLα silencing in MATa cells leads to loss of mating type identity and loss of mating ability. Cells were plated in 10-fold serial dilutions on selective synthetic media. Diploids that result from effective mating were ADE2 + LEU2 + and able to grow on –ADE –LEU media. C) Telomeric silencing was examined in a strain (UCC7164) containing a telomeric URA3 reporter (TEL-VII-L) and telomeric ADE2 reporter (ADE2-TEL-VR). Plasmid-based Dot1 expression was induced with 3% galactose53. Cells were plated in 10-fold serial dilutions on selective synthetic media with or without 5-FOA. Cells that silence URA3 can grow on 5-FOA media whereas cells that express URA3 cannot. Cells that silence ADE2 accumulate a red pigment whereas cells that express ADE2 are white. TbDot1A G138A and TbDot1B G121A show H3K79 methylation activity, while TbDot1A 138R and TbDot1B G121R have lost their ability to methylate H3K7953. D) Yeast strains expressing yDot1, no Dot1, partially active yDot1 (ΔN and G401A)21, TbDot1A or TbDot1B were plated in 10-fold dilution series on rich media with or without 100 mM hydroxyurea (HU). Loss of mating type identity by TbDot1A or –B expression (see panel B) was eliminated by deletion of the HMLα1/2 genes.