Fig. 4.
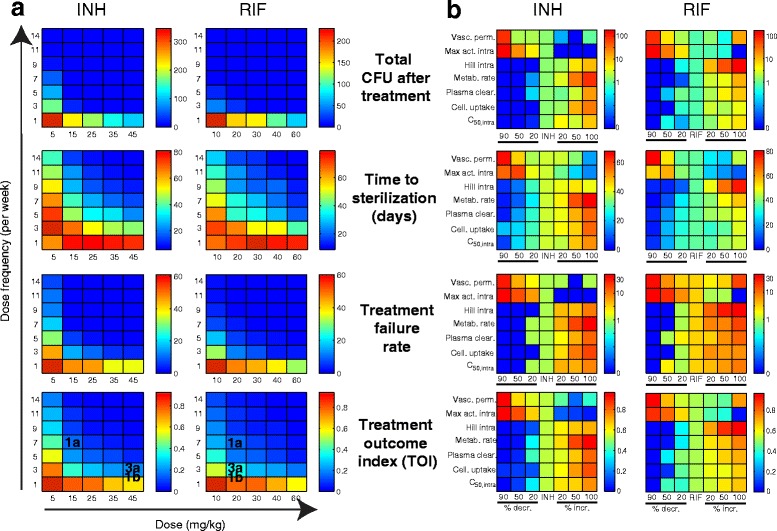
Evaluating antibiotics and regimens improvements. Color scales: means (N = 82) for total CFU after treatment, time to sterilization, treatment failure rate and TOI. Red: poor outcomes; blue: good outcomes; dark blue: optimum outcomes. a Varying dose (INH: 5–45 mg/kg; RIF: 10–60 mg/kg) and dose frequency (1–14 doses per week). Regimens from Fig. 1b are noted on bottom. b Modifying PK-PD properties (vertical axes) previously identified [20] to affect outcomes. Results for INH-1a/RIF-1a (center columns on all panels) are compared with antibiotics where properties were decreased (by 20, 50 or 90 %, left of center) or increased (by 20, 50 or 100 %, right of center) from INH/RIF values. Y-axes show parameters: vascular permeability; maximum killing activity against intracellular Mtb; Hill constant quantifying steepness of dose response killing curve for intracellular Mtb; rate of antibiotic metabolism inside host cells; rate of antibiotic clearance from plasma; Cellular uptake ratio; concentration of antibiotic where 50 % of maximum killing activity is achieved against intracellular Mtb
