FIG 2.
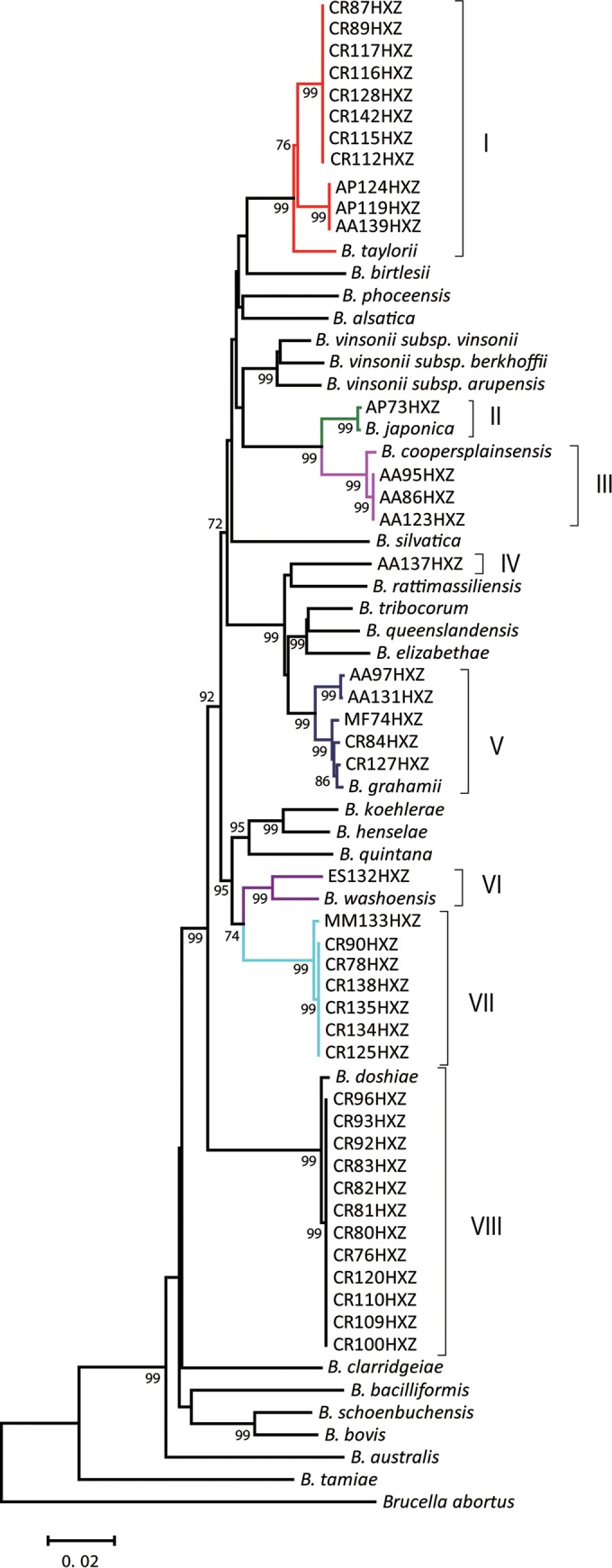
Phylogenetic relationships of the Bartonella type strains and the Bartonella isolates from Heixiazi Island based on the concatenation of fragments of gltA, the 16S rRNA gene, ftsZ, and rpoB. The phylogenetic tree was inferred using the neighbor-joining method based on the Kimura 2-parameter model in MEGA6 (13). The percentages of replicate trees (>70%) in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1,000 replicates) are shown next to the branches. The analysis involved 3,110 concatenated nucleotides from 68 isolates. Roman numerals I to VIII on the right side of the tree correspond to different Bartonella genetic groups. Homologous sequences of Brucella abortus were used as an outgroup. All sequences were trimmed to the same size, and gaps were excluded from the analysis.
