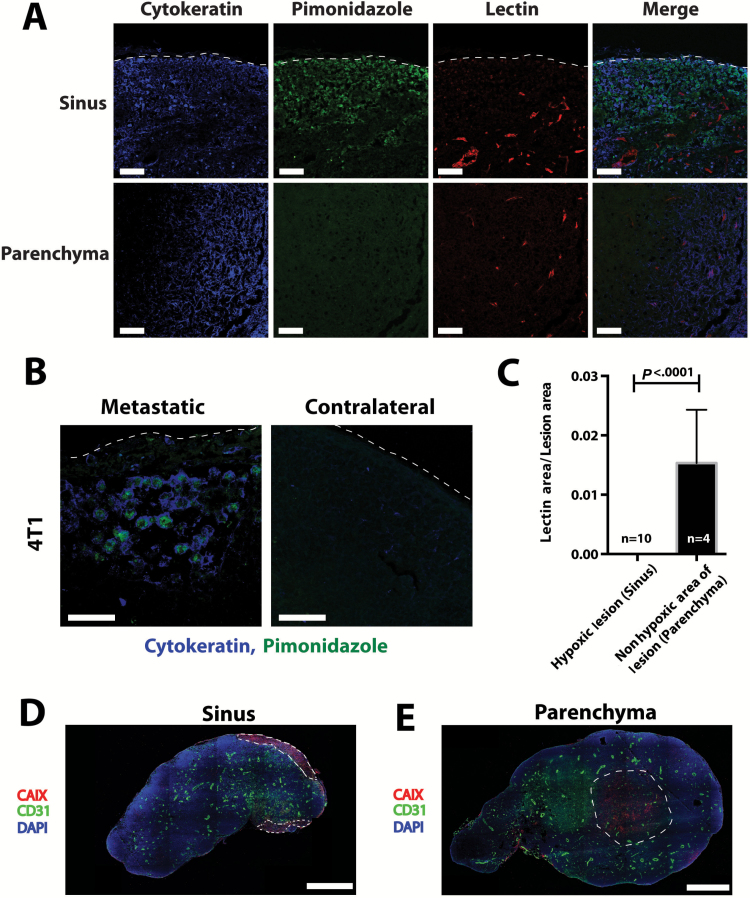
Figure 4.
Hypoxia in lymph node metastases. A) Representative images of pimonidazole staining for hypoxia (green) and perfused lectin staining for functional blood vessels (red) in lymph node metastases from 4T1 mammary carcinoma (cytokeratin, blue). The top panels show a lesion in the subcapsular sinus that is hypoxic and has no perfused blood vessels in the lesion. The bottom panels show a lesion in the parenchyma of the lymph node with perfused blood vessels and no hypoxia. Dashed line shows edge of the lymph node. Scale bars = 100 μm. B) Higher magnification of pimonidazole staining in metastatic lymph node showing colocalization of cytokeratin and pimonidazole. Contralateral lymph node is non–tumor bearing. Dashed line shows edge of the lymph node. Scale bars = 50 μm. C) Quantification of pimonidazole and perfused vessel staining in metastatic lesions in the subcapsular sinus and lymph node parenchyma. Data are presented as mean ± 95% confidence interval. Statistical significance was tested by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. D and E) Staining for CAIX, a marker of the cellular response to hypoxia, and CD31-positive blood vessels shows similar results to pimonidazole staining. Dashed line shows the outline of the metastatic lesions. Scale bars = 636 μm.