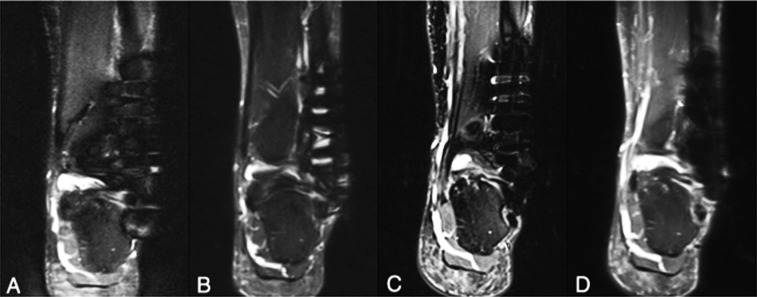
Figure 6.
A patient with stainless steel plate and six stainless steel screws placed for a Weber C fracture was imaged at 1.5 T (a, b) and 3.0 T (c, d) using short tau inversion recovery conventional sequence (a, c) and slice encoding for metal artefact correction with view angle tilting (SEMAC-VAT) technique (b, d). At both field strengths, a substantial reduction in metal artefact was achieved with SEMAC-VAT, on which the assessment of periprosthetic structures becomes possible. As noted, however, the image quality with SEMAC-VAT at 3.0 T seems better than at 1.5 T owing to higher signal-to-noise ratio, even though the artefact size is larger at 3.0 T.