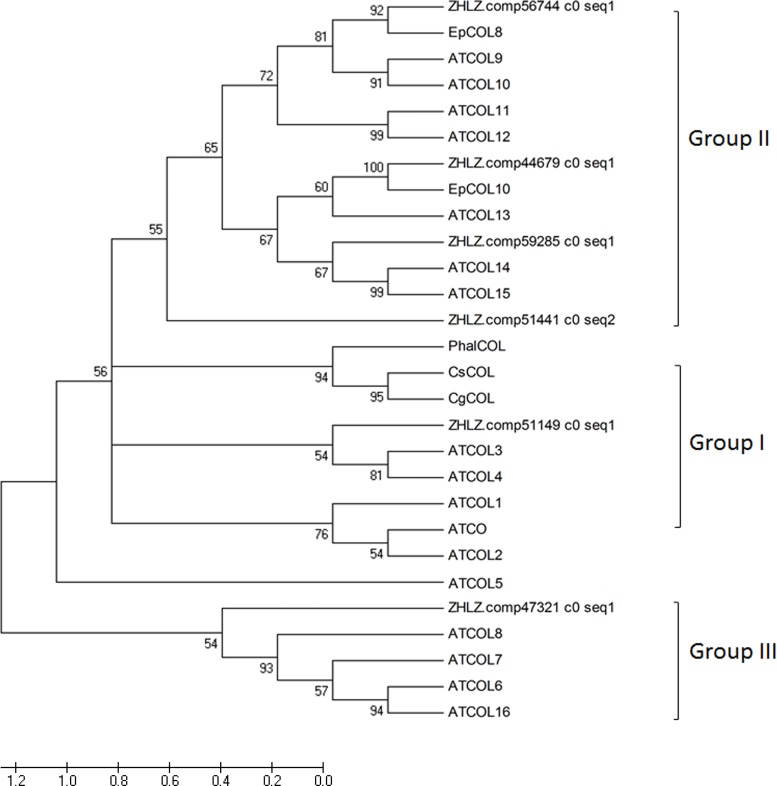
Fig 6. Phylogenetic analysis of the CONSTANS-like proteins from different plant species.
Amino acid sequences were aligned by the ClustalW 2.0, and phylogenetic relationships were reconstructed using a maximum-likelihood (ML) method in PHYML software with JTT amino acid substitution model. Bootstrap values for 1,000 replicates were used to assess the robustness of the trees. Previously published plant MADS-box protein sequences were retrieved from GenBank database. (AtCO: NP_197088, AtCOL1: NP_197089, AtCOL2: NP_186887, AtCOL3: Q9SK53, AtCOL4: Q940T9.2, AtCOL5: Q9FHH8, AtCOL6: Q8LG76, AtCOL7: Q9C9A9, AtCOL8: Q9M9B3, AtCOL9: NP_001118599, AtCOL10: Q9LUA9, AtCOL11: O23379, AtCOL12: Q9LJ44, AtCOL13: O82256, AtCOL14: O22800, AtCOL15: Q9C7E8, AtCOL16: Q8RWD0, PhalCOL: FJ469986, CsCO: GU168786. EpCOL8: KC836891.1, EpCOL10: KC836893.1)