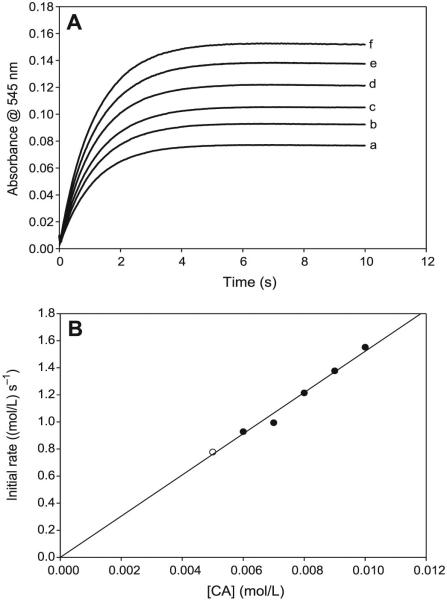
Fig. 4.
(A) Absorbance traces showing the effect of varying cysteamine hydrochloride (CA) concentrations. The reaction displays first-order kinetics in CA. [NO2−]0 = 0.10 mol/L; [H+]0 = 0.10 mol/L; and (a) [CA]0 = 0.005 mol/L; (b) [CA]0 = 0.006 mol/L; (c) [CA]0 = 0.007 mol/L; (d) [CA]0 = 0.008 mol/L; (e) [CA]0 = 0.009 mol/L; and (f) [CA]0 = 0.010 mol/L. (B) Initial rate plot of the data in Fig. 4A. The plot shows the strong first-order dependence of the rate of formation of S-nitrosocysteamine (CANO) on CA, with an intercept kinetically indistinguishable from zero.