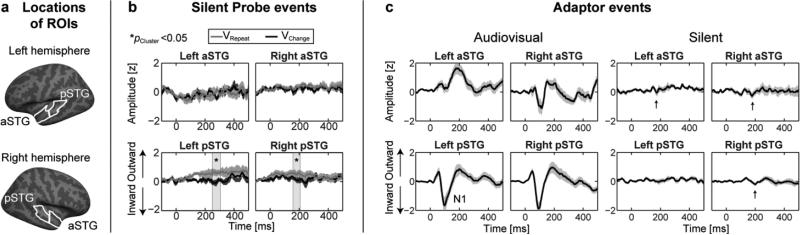
Figure 3.
AC ROI time course analysis during silent movie clips. (a) Locations of ROIs. (b) ROI time course analysis of silent Probe events. The visual stimulus alone resulted in a slow positive drift for the AVRepeat condition in pSTGs. However, the observed effects were spatially and temporally different from the effects of the main experiment, as the time courses in left aSTG, where the most significant modulations were observed in the main experiment, were virtually similar across the respective conditions of the control experiment. No significant differences were observed in the average N1 amplitude during the 50–150 ms time window. The time courses are normalized for display to the same scale than the corresponding time courses in Fig 2c. (c) AC ROI time course analysis of Adaptor responses during audiovisual and silent movie clips. Consistent with our previous studies (Raij et al., 2010), weak onset responses that share resemblance to the N1 response were observed even to silent Adaptors (marked with an arrow). The time courses are normalized for display by the standard deviation of responses within each ROI during the audiovisual condition. In the panels b and c, the error bars indicate the standard error of mean across subjects at each time point.