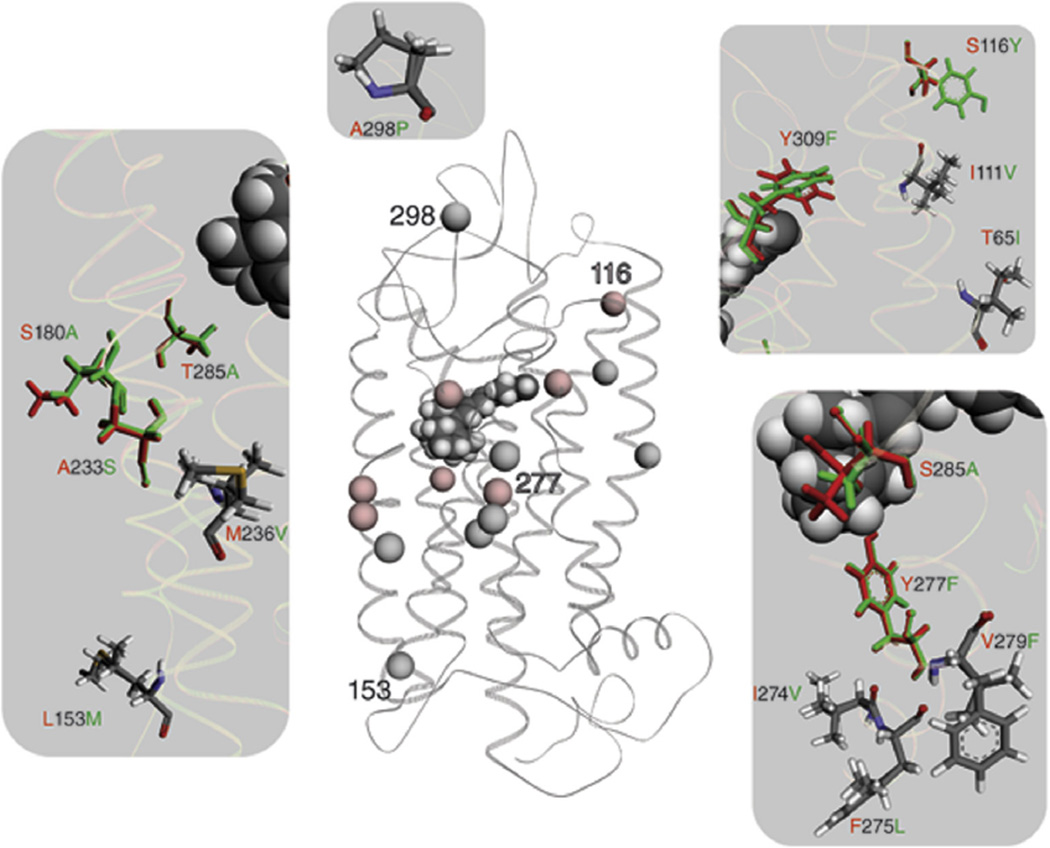
Fig. 4.
A structural comparison between the L/LWS and M/LWS opsin model is shown. Wire representation of the L/LWS and M/LWS model is based on the rhodopsin crystal structure. Spheres illustrate differences in the amino acid sequence between L/LWS and M/LWS. Red spheres indicate differences responsible for spectral tuning between L/LWS and M/LWS, whereas gray spheres do not contribute to color tuning, according to (Asenjo et al., 1994). Numbers within the LWS model help to orient between the magnifications and the GPCR overview. Fifteen changes in amino acid residues are magnified on a gray background; amino acid residues contributing to color tuning are in their corresponding colors, namely red for L/LWS and green for M/LWS. Changed amino acid residues that do not affect spectral tuning are colored according their atoms.