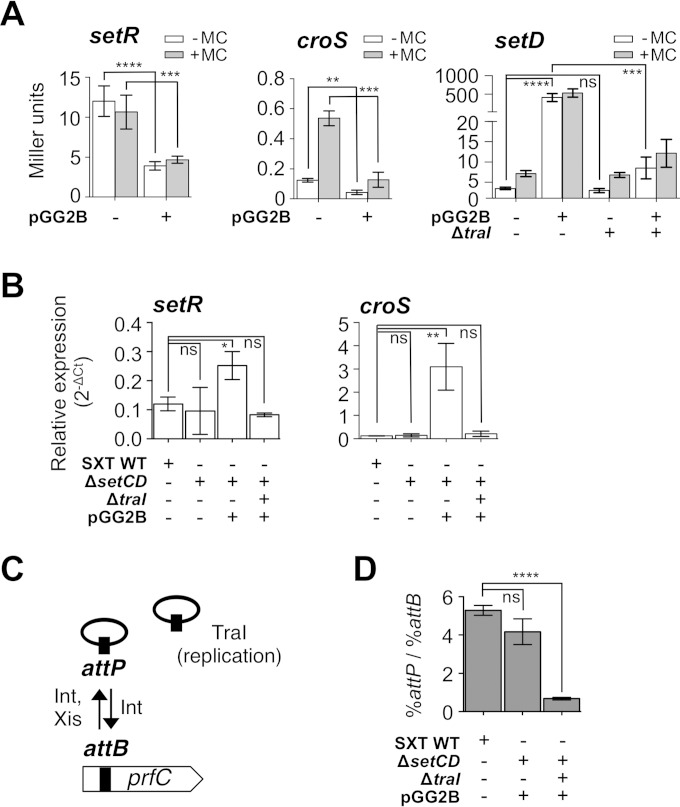
FIG 5.
Overexpression of setCD leads to an indirect positive feedback loop boosting the expression from PL and PR. (A) Effect of SetCD on the expression of setR, croS, and setD translationally fused to lacZ measured by β-galactosidase assay in the presence or absence of MC. The strains contain pSRZ (DPL246), pSZR (DPL241), SXT setD′-′lacZ ΔsetC (DPL297), or SXT ΔtraI setD′-′lacZ ΔsetC (DPL548). Overexpression assays were carried out by expressing setCD from the arabinose-inducible PBAD promoter in pGG2B. (B) Effects of setCD deletion and overexpression on setR and croS mRNA levels. qRT-PCR assays were carried out with E. coli BW25113 carrying SXT (VB17, WT [wild type]) or its ΔsetCD or ΔtraI ΔsetCD (DPL297 and DPL548) derivative without MC induction. Overexpression assays were carried out by expressing setCD from pGG2B. (C) Representation of integration/excision and replication of SXT. (D) Measurement of SXT copy number by qRT-PCR (percent attP/percent attB with prfC as a reference) in SXT derivatives (identical to those in panels A and B) with or without overexpression of setCD. Each bar represents the mean and standard deviation of values from three independent experiments. Statistical analyses of the mean values were performed with two-tailed unpaired t tests, with the exception of the setD results in panel A, for which the logarithms of the mean values were used. Statistical significance is indicated as follows: ns (not significant), P > 0.05; *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001; ****, P ≤ 0.0001.