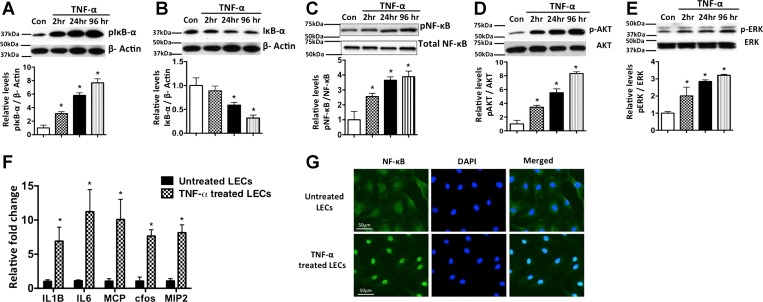
Fig. 1.
TNF-α-mediated inflammatory signaling in lymphatic endothelium. A–E: representative Western blots of protein samples from lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) exposed to TNF-α (20 ng/ml) for 2, 24, and 96 h and probed with phosphorylated (p-) and total forms of IκB, NF-κB, Akt, and ERK. Experiments were carried out in triplicates. β-Actin was used as endogenous housekeeping control. Quantitative values obtained from each experiment are shown below each blot. *P < 0.05 vs. control (Con). F: induction of inflammatory cytokines in inflamed lymphatics. TNF-α induces key proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β, IL-6, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1), c-fos, and macrophage inflammatory protein 2 (MIP-2), in LECs. LECs were treated for 24 h with TNF-α (20 ng/ml). Real-time quantification was carried out, and fold change relative to untreated control was calculated. Experiments were done in triplicates. Values are means ± SE. *P < 0.05. G: immunofluorescence image of activated NF-κB translocation into nucleus in LECs; 4′,6′-diaminido-2-phenylindole (DAPI) was used for nuclear staining. Magnification ×40. Scale bar = 50 μm.