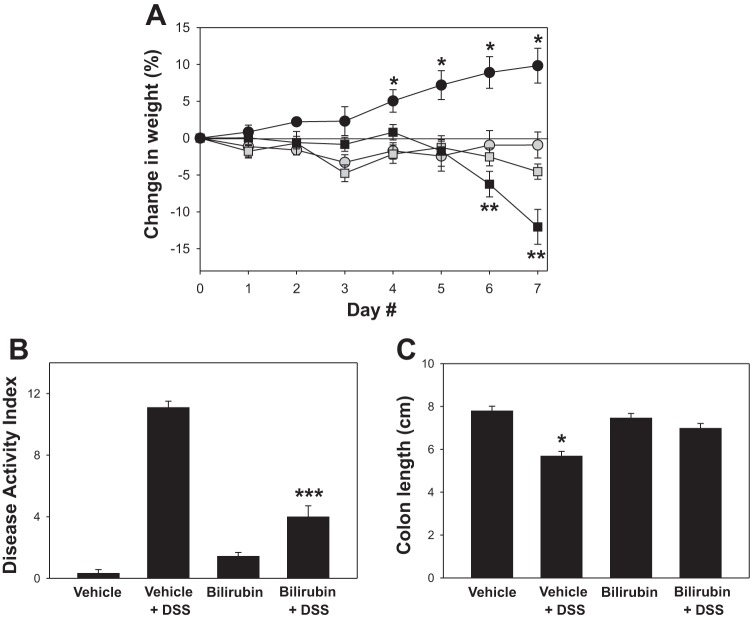
Fig. 1.
Effect of bilirubin on body weight, disease activity, and colonic shortening induced by dextran sodium sulfate (DSS). Mice were administered 2.5% DSS in the drinking water, followed by intraperitoneal injections of bilirubin (shaded squares) or the potassium phosphate vehicle (black squares). Control animals received bilirubin (shaded circles) or vehicle (black circles) without DSS. A: average daily percent change in weight from baseline (±SE) following the initiation of DSS. B: mean disease activity index for each group. C: average length of resected colon specimens. Compared with the other treatment groups, the colons from mice treated with DSS plus vehicle were significantly shorter and lacked formed stool. *P < 0.002 vs. all other groups, **P < 0.03 vs. bilirubin and bilirubin + DSS, ***P < 0.001 vs. vehicle + DSS.