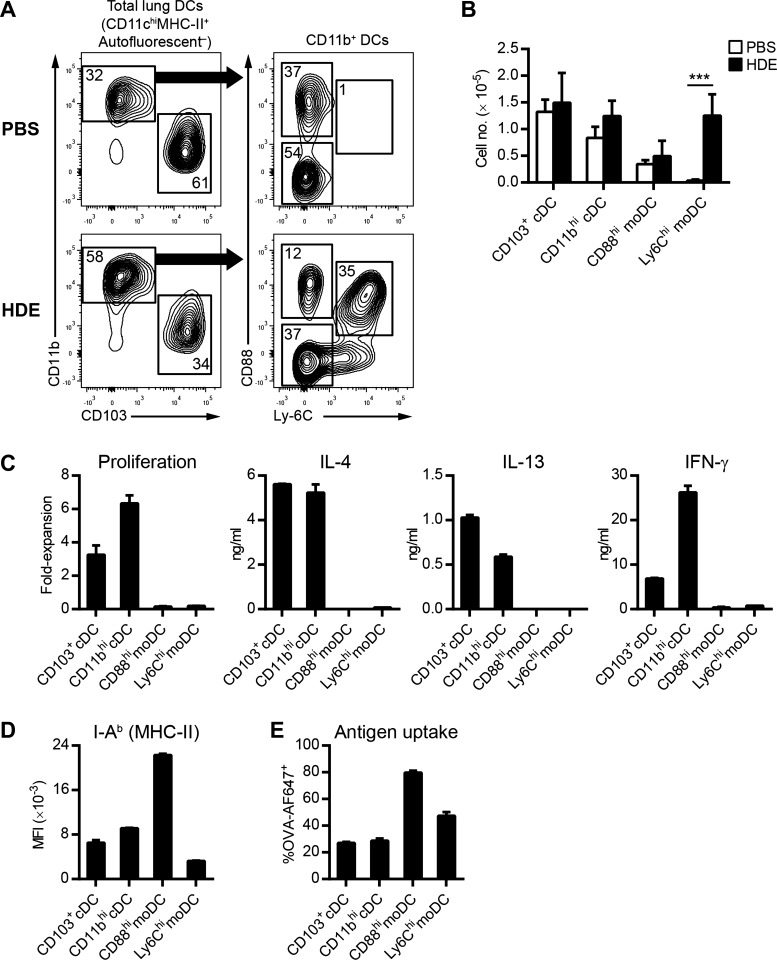
Fig. 1.
Lung conventional dendritic cells (cDCs), but not monocyte-derived DCs (moDCs), induce T helper 2 (Th2) differentiation following house dust extract (HDE) exposure. A: flow cytometric analysis of lung DC subsets 16 h after airway installation of HDE or PBS. Numbers represent the frequency of cells within each gate. Data are from a single experiment, representative of 4 experiments. B: total number of individual lung DC subsets in C57BL/6 mice following HDE (solid bars) or PBS (open bars) exposure. Bars represent the means ± SD of combined data from 4 experiments. C: Th cell polarization by lung DCs. The indicated lung DC subsets were isolated from C57BL/6 mice by flow cytometry 16 h after instillation of HDE/ovalbumin (OVA) and cultured with naive CD4 T cells prepared from OT-II mice to induce Th cell differentiation. Bars represent the means ± SD of duplicate wells. Data are from 1 experiment, representative of 4 experiments. D: flow cytometric analysis of I-Ab (major histocompatibility complex II, MHC-II) expression on lung DCs following airway installation of HDE. Bars represent the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) ± SD (n = 3 mice per group). Data are from a single experiment, representative of 2 experiments. E: flow cytometric analysis of lung DCs following airway installation of HDE and fluorescent OVA-AF647 antigen. The graph depicts the percentage of DCs that have taken up OVA-AF647 antigen. Bars represent the means ± SD (n = 3 mice per group). ***P < 0.001.