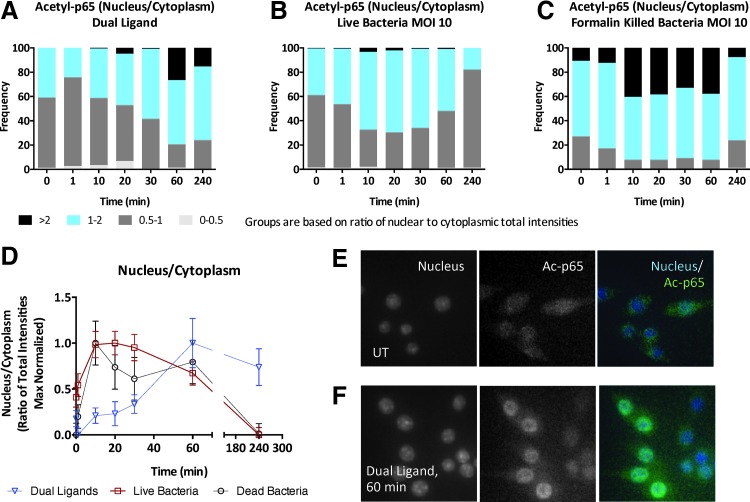
Fig. 2.
Imaging dual TLR and bacterial infection-induced nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cell (NF-κB) response in mouse macrophages. WT IMMs were either (A) stimulated with dual TLR ligands—10 nM each of P3C and lipid A—or (B, C) infected with live or formalin-killed B. cenocepacia J2315 at MOI 10 for up to 4 h and the ratio of nuclear to cytoplasmic intensity of acetylated-p65 (Ac-p65) was calculated. (D) The median nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratios of Ac-p65 normalized to maximum. (E, F) Images at 20× magnification captured by the CellInsight NXT are shown for untreated and dual ligand treatment for 60 min. Data shown are representative of two independent experiments (D; median+median absolute deviation), and number of cells imaged were 1,930 cells for dual TLR ligand treatment, 2,228 cells for live bacterial infection, and 2,167 cells for killed bacterial infection.