Figure 1.
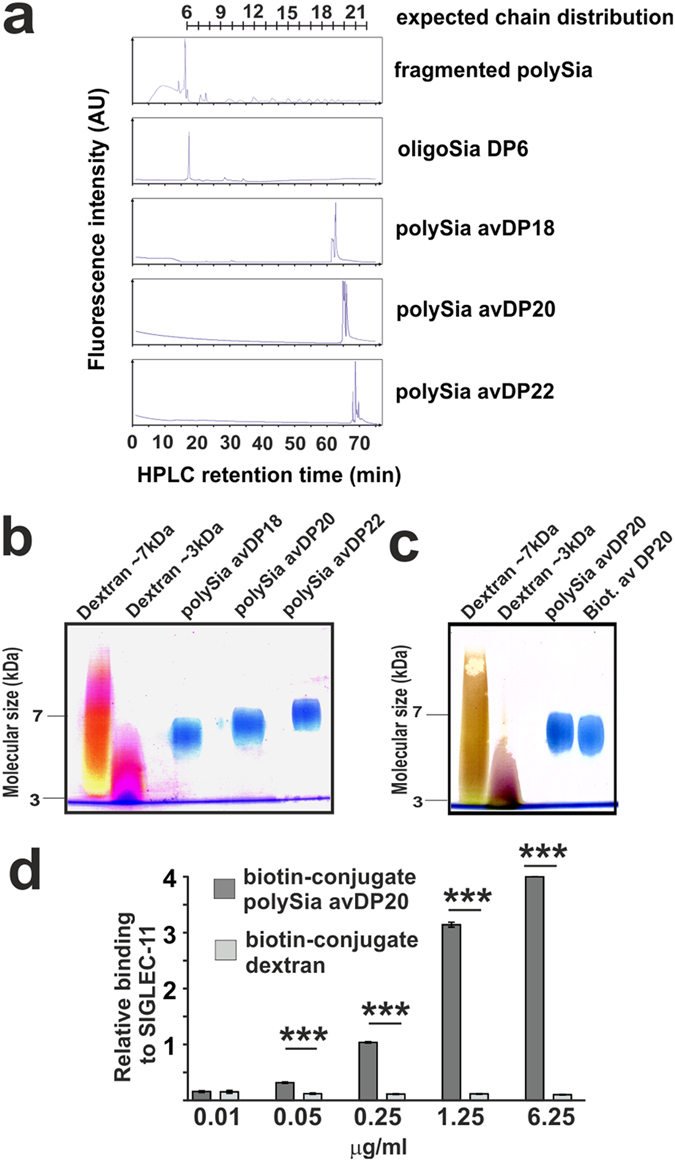
(a) HPLC analysis of oligoSia with a degree of polymerization of 6 (oligoSia DP6) and polySia with average degree of polymerization 18, 20 and 22 (polySia avDP18, avDP20 and avDP22) compared to hydrolyzed polySia. DMB-labeled oligoSia DP6, polySia avDP18, avDP20 and avDP22 were eluted by a NaCl buffer gradient. The HPLC retention times were monitored. (b) Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of polySia avDP18, avDP20 and polySia avDP22 visualized by stains-all solution. PolySia avDP20 showed a molecular weight of ~6 kDa. Dextran sulfate with molecular weights of ~3 kDa and ~7 kDa served as molecular weight controls. Representative image out of at least three independent experiments is shown. (c) Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of biotinylated polySia avDP20 (Biot. av DP20) visualized by stains-all solution. Majority of biotinylated polySia avDP20 is still intact after biotinylation. Representative image out of at least three independent experiments is shown. (d) ELISA to demonstrate the interaction between polySia with avDP20 and SIGLEC-11. SIGLEC-11 Fc-fusion protein was coated to an ELISA plate. Biotinylated polySia avDP20 (0.01, 0.05, 0.25, 1.25 and 6.25 μg/ml) or biotinylated dextran (0.01, 0.05, 0.25, 1.25 and 6.25 μg/ml) were added and detected by HRP conjugated streptavidin, followed by a TMB reaction. PolySia avDP20 bound to SIGLEC-11 Fc-fusion protein, while there was negligible binding of biotinylated dextran. Data are presented as relative binding (values of OD 450 measurements) mean +/− SEM of n = 3 independent experiments. ***p < 0.001; ANOVA followed by Bonferroni.
