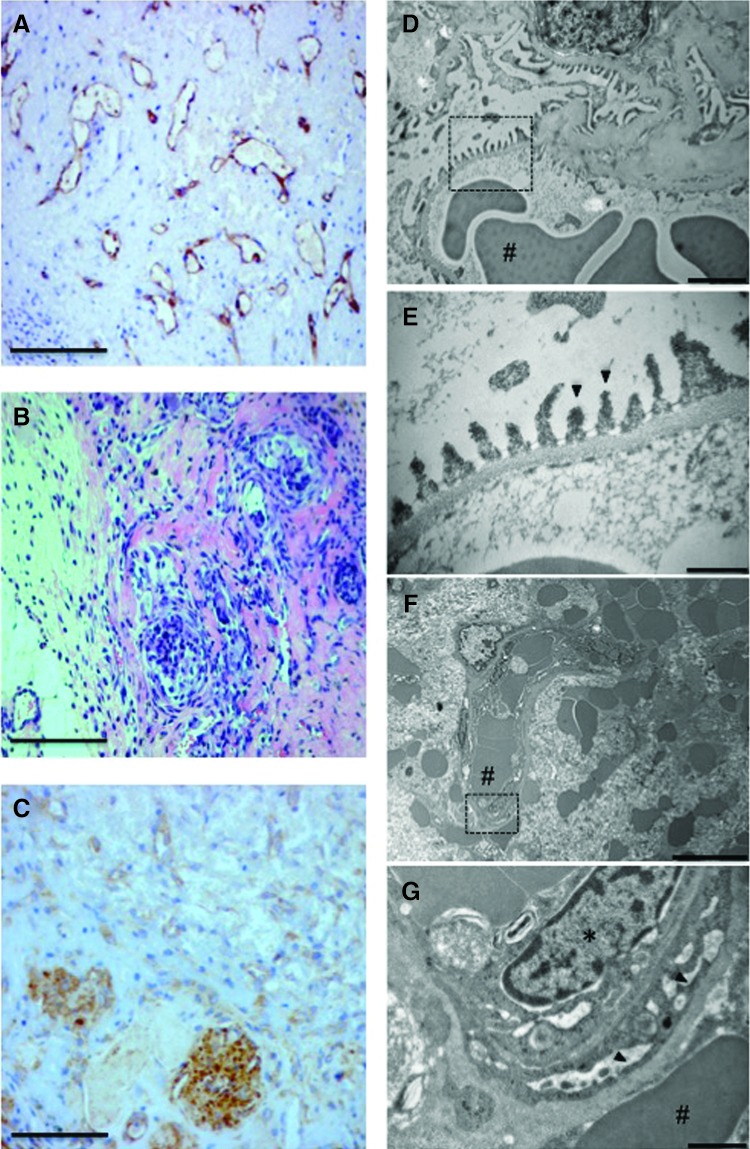
FIG. 4.
Histology and ultrastructure of implanted gels with Bcl-2-ECs and glomeruli. (A) Human endothelial CD31 staining (brown) and hematoxylin counterstain (blue). (B) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of cluster of glomeruli. (C) Staining for podocytes with rat podocin antibody (brown) and hematoxylin counterstain (blue). Scale bars for (A–C) are 100 μm. (D–G) Transmission electron microscopy of normal rat and glomeruli implanted with Bcl-2-ECs at 2 weeks. (D) Capillary loops and basement membrane of normal rat glomerulus. Scale bar is 2 μm. (E) Higher magnification of dashed area (D) demonstrating podocyte foot processes and basement membrane of normal glomerulus. Scale bar is 0.5 μm. (F) Microvessels containing red blood cells formed within the collagen gels containing Bcl-2-ECs. Scale bar is 10 μm. (G) Higher magnification of dashed area (F) demonstrating implanted glomerulus with red blood cells, endothelial swelling, and podocyte effacement. Scale bar is 1 μm. * Indicate nuclei and arrows indicate podocyte foot processes. # Indicate red blood cells in the glomerulus.