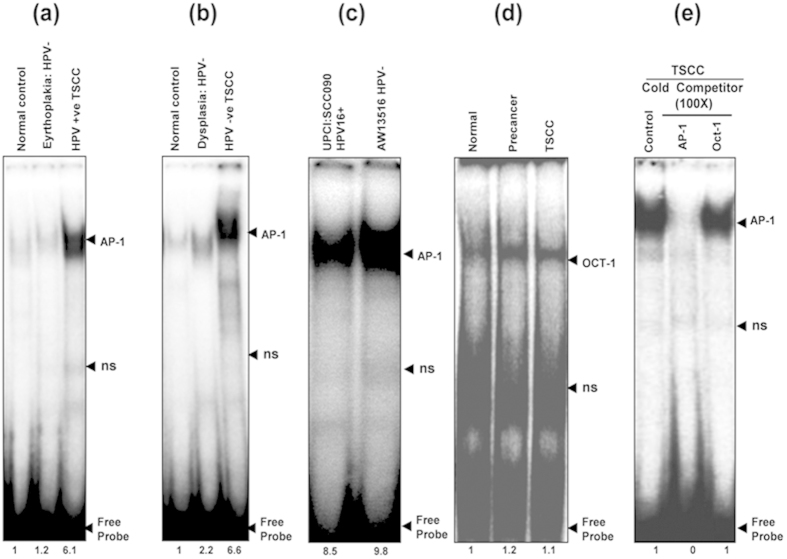
Figure 1.
(a–e): Constitutive activation and higher DNA binding activity of AP-1 in HPV+ve and HPV−ve tongue tumor tissues and cell lines. EMSA showing DNA binding activity of AP-1 in nuclear extracts (10 μg) of different grades of tongue tissues (a,b) and cell lines (c) using γ32P- ATP-radiolabeled oligonucleotide harboring an AP-1 consensus sequence. Increasing AP-1 binding activity was observed as the severity of tongue lesions progressed from normal to precancer to invasive cancer in both HPV16+ve (a) and HPV−ve (b) cases. Both HPV16+ve UPCI:SCC090 and HPV−ve AW13516 (c) cell lines showed higher binding activity of AP-1. (d) EMSA with labeled Oct-1 probe showed uniform DNA binding in all grades of tongue tissues. Binding specificity was evidenced in a competition assay with nuclear extracts of TSCCs incubated with unlabelled 100 molar excess of specific competitor AP-1 probe and nonspecific competitor Oct-1 probe (e). Fold change in the band intensities of AP-1 are indicated in each lane. Ns: non-specific binding.