Fig. 1.
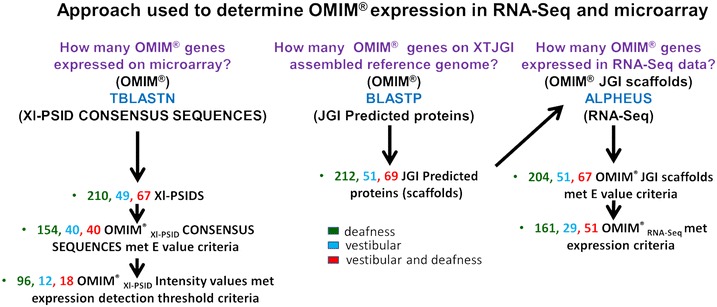
Experimental strategy for determining the expression of OMIM® orthologues for deafness and vestibular disorder genes in the Xenopus inner ear transcriptome with Illumina-Solexa (RNA-Seq) and Affymetrix microarray methods. A comprehensive list of OMIM® genes for deafness and vestibular genes was manually curated and used to map OMIM® sequences to the Xl-PSIDs on the Affymetrix GeneChip ® X. laevis Genome Array, and to the JGI Xenopus reference genome scaffolds. Xenopus inner ear RNA was used in microarray hybridization reactions with the Affymetrix GeneChip ®. The hybridization data were analyzed to retrieve intensity values from target Xl-PSIDs that had met alignment criteria for OMIM® orthologues for deafness and vestibular disorder genes. The Alpheus® program was implemented to map inner ear RNA-Seq reads to the JGI Xenopus reference genome scaffolds and the RNA-Seq alignment data were analyzed to retrieve target scaffold regions that had met alignment criteria for OMIM® orthologues for deafness and vestibular disorder genes. As part of the analysis, the data were separated into three OMIM® phenotype categories: deafness only; vestibular disorder only; and both deafness and vestibular disorder. When expression criteria were applied to both datasets, RNA-Seq methods detected expression of more OMIM® orthologues for deafness and vestibular disorder genes in the Xenopus inner ear (241) than were detected by microarray methods (126)
