Figure 7.
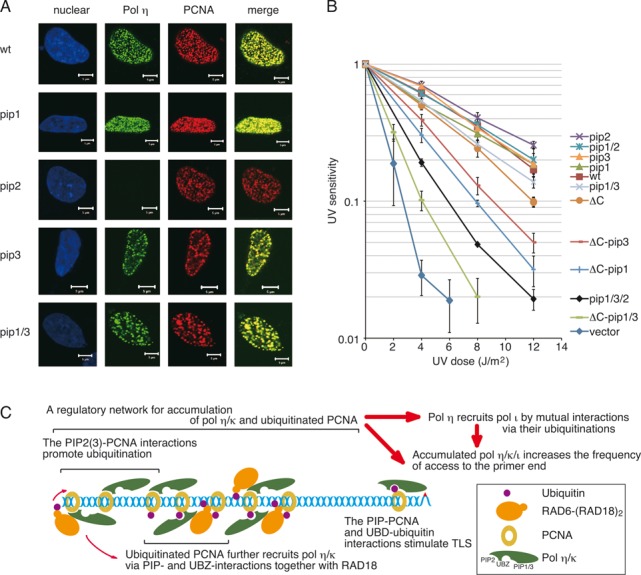
Cellular functions of the motifs of Polη. (A) Co-localization of Polη with PCNA. XP-V cells were transiently transfected with plasmids encoding wild-type FLAG-Polη or the indicated mutants. After UV irradiation, FLAG-Polη and PCNA were visualized by immunostaining with anti-Polη and anti-PCNA antibodies, respectively. Nuclei were stained by Hoechst 33342. Scale bars represent 5 μm. Control experiments confirming expressions of FLAG-Polη were shown in Supplementary Figure S7. (B) UV sensitivities of XP-V cells stably expressing FLAG-Polη. Cells were irradiated with the indicated dose of UVC, incubated with 1 mM caffeine for 4 days, and their viabilities were measured. Error bars show SD from three independent experiments. (C) A model for a regulatory network for foci formation and the TLS function of Polη/ι/κ. Interactions of Polη/κ with PCNA, together with RAD6-(RAD18)2, leads to their accumulation by promoting mono-ubiquitination of PCNA around stalled 3′-OH ends. Interactions of Polη/ι/κ with mUb-PCNA via PIPs and UBDs stimulate DNA synthesis at stalled 3′-OH ends. See text for details.
