Figure 3.
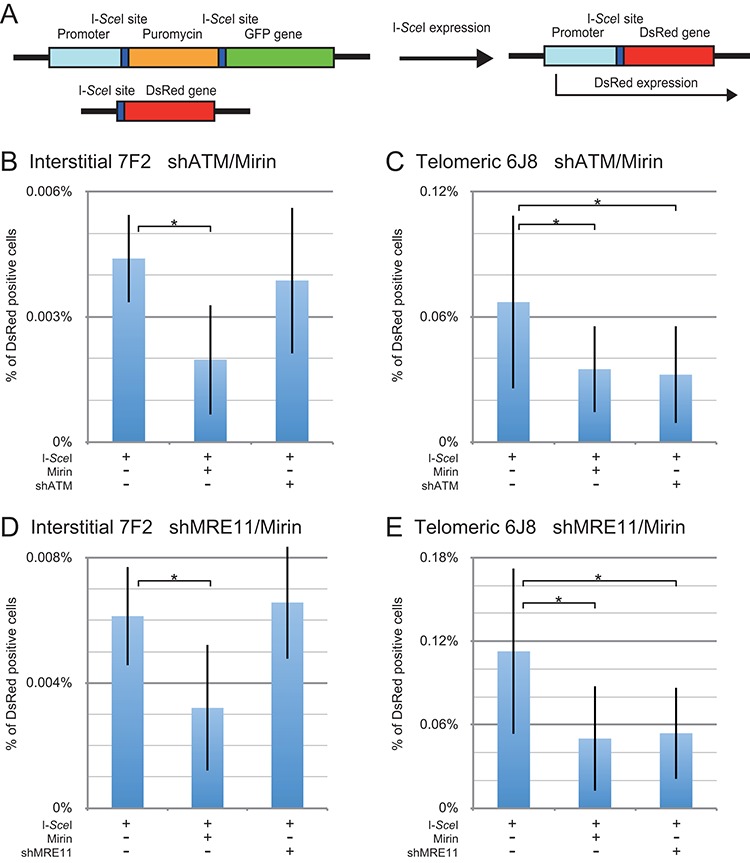
The effect of inhibition of MRE11 and ATM on GCRs at interstitial and subtelomeric DSBs. (A) The analysis of GCRs was performed using cell clones that contain the pEJ5-GFP plasmid integrated at an interstitial (EDS-7F2) or telomeric (EDS-6J8) site, and a pDsRed-ISceI plasmid integrated at an interstitial site. The DsRed gene in the pDsRed-ISceI plasmid is initially inactive due to the lack of a promoter, but is activated following NHEJ between the I-SceI-induced DSBs in the pEJ5-GFP and pDsRed-ISceI plasmids. The frequency of GCRs (DsRed-positive cells) at the I-SceI-induced DSB was determined for clone EDS-7F2 (B, D) and clone EDS-6J8 (C, E) following infection with the pQCXIH-ISceI retrovirus vector and selection with hygromycin for 14 days for EDS-7F2 and 15 days for EDS-6J8. GCRs were analyzed following (B, C) treatment with Mirin or knockdown of ATM (shATM), or (D, E) treatment with Mirin or knockdown of MRE11 (shMRE11). Control cultures for knockdown of ATM or MRE11 were treated with shRNA-mediated knockdown of luciferase, while control cultures for Mirin were treated with DMSO. The values shown in the graph represent the average of more than three independent experiments, each done in triplicate (see Supplementary Figures S3 and S4, and Table S1 for raw data). Error bars represent the standard deviation of the more than three separate experiments. Statistical significance for comparisons between the indicated values (horizontal lines) was determined using the two-tailed Student's t-test, and an asterisk indicates statistically significant values of 0.05 or less.
