Figure 1.
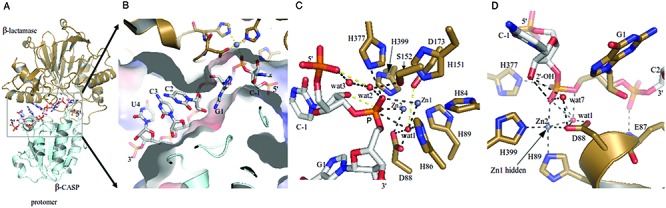
The RNA binding channel in S. coelicolor RNase J (SCO5745), and a sequential zoom to the active site from the structure of the pre-cleavage complex formed with RNA. (A) Single stranded RNA is engaged at the interface between the β-CASP and β-lactamase domains. Only one protomer of the RNase J tetramer assembly is shown for clarity. The protein and RNA are shown in cartoon and stick representations, respectively. (B) The RNA binding tunnel (surface representation) with bound nucleic acid (in stick representation). Some amino acids in the active site are shown in stick representation. The surface is colored blue for positive regions and red for negative regions. (C) A view of the active site, showing details of interactions between waters and the scissile phosphate. The key hydrogen bonding interactions and zinc contacts with the RNA are shown as dashed lines. Residues that coordinate the two Zn-ions are shown in stick representation. (D) Substrate backbone interaction network at the active site. The view shows the participation of the D88 side chain in the water network at the active site and the amide of E87 in phosphate binding as well as the interaction of the 2′ OH of the terminal base with the scissile phosphate. In relation to Figure 1C, the perspective involves rotation about the vertical axis. These and other figures use the following color scheme: oxygen in red, nitrogen in blue, phosphate in orange, carbon in gray, Zn as gray spheres, and water as red spheres.
