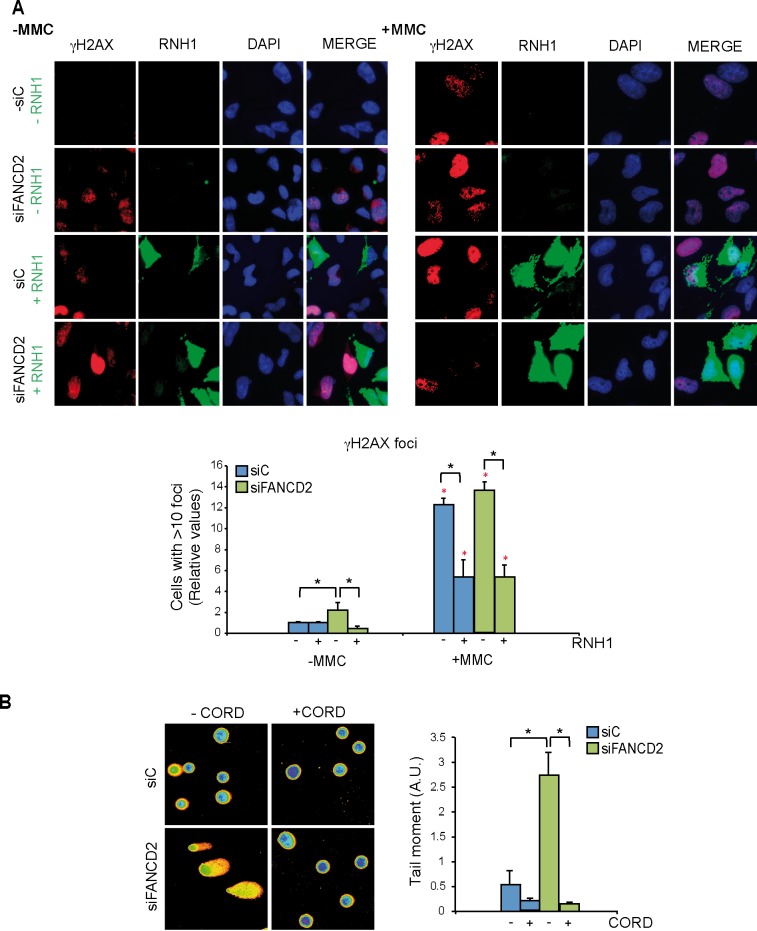
Fig 4. Genome instability in FANCD2-depleted human cells.
(A) Detection of γH2AX foci by IF in siC and siFANCD2 HeLa cells transfected with pcDNA3 (-RNH1) or pcDNA3-RNaseH1 (+RNH1) for RNase H1 overexpression and either untreated or treated for 16 h with 80 ng/ml mitomycin C (MMC). Nuclei were stained with DAPI. The graph shows the quantification of the relative amount of cells containing >10 γH2AX foci with respect to the siC in each case. More than 100 cells overexpressing RNase H1 (positive-stained) or more than 100 cells of mixed population transfected with the empty vector were counted in each of the three experiments. Data represent mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. The red asterisks refer to the comparison of each MMC-treated samples versus its own untreated sample. *, P < 0.05 (Mann-Whitney U test). As a reference the percentage of cells with ≥10 γH2AX foci is >75% in siC cells treated with MMC (B) DNA breaks measured by single-cell gel electrophoresis (comet assay) of siC and siFANCD2 HeLa cells treated or untreated for 4 h with 50 μM cordycepin. The graph shows the median comet tail moment. More than 100 cells were counted in each of the three experiments. Data represent mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05 (Student’s t-test).