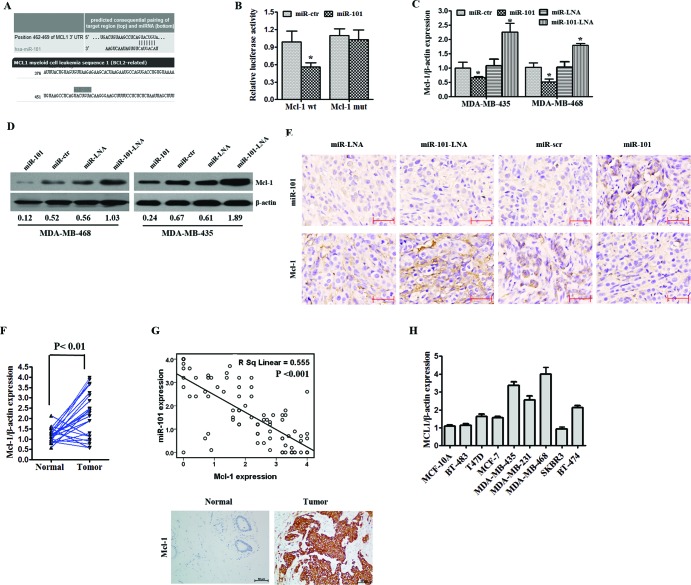
Figure 4. MiR-101 directly targets MCL-1.
A. MiR-101 was predicted to bind to the MCL-1 3′-UTR using TargetScan and microRNA online software. B. A luciferase assay was performed on MDA-MB-435 cells co-transfected with miR-101 mimics, a scrambled control, miR-101 inhibitors, a control and a luciferase reporter containing MCL-1 3′-UTR (MCL-1-wt) or mutant constructs in which the five nucleotides of the miR-101 binding site were mutated (MCL-1-mut). An empty luciferase reporter construct was used as a negative control. *p < 0.05 vs. scramble. C. MDA-MB-435 and MDA-MB-468 cell lines were transfected with miR-101 mimics, miR-101 inhibitors or their controls. The mRNA expression of MCL-1 was detected by qRT-PCR. D. The effect of miR-101 mimics or miR-101 inhibitors on the protein expression of MCL-1 was determined by Western blot in both the MDA-MB-435 and MDA-MB-468 cell lines. β-actin was used as a loading control. E. In situ hybridization was used to detect the expression of miR-101, and immunohistochemistry was used to detect the expression of MCL-1 in transplanted tumor tissues in the scramble, miR-101 mimics, control and miR-101 inhibitor groups. F. The expression of MCL-1 in 22 paired TNBC specimens and the corresponding paired normal, adjacent tissues are shown in a column analysis. G. The correlation between miR-101 and MCL-1 expression in breast cancer tissues was analyzed by comparing miRNA and mRNA expression. H. The expression of MCL-1 was determined by qRT-PCR in one normal mammary cell line, five tumor cell lines with a luminal transcriptional profile and three tumor cell lines with a basal-like transcriptional profile. miR-101 expression was normalized using U6 RNA expression. Error bars represent standard deviations (SD) for three replicates in one experiment.