Figure 2. NLK regulates proliferation and stem cell-like properties in patient-derived primary GBMs.
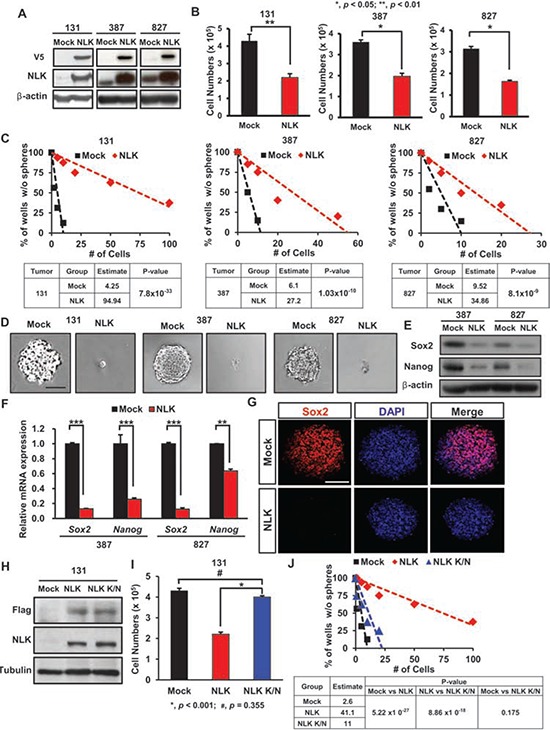
A. Immunoblots of V5-NLK and NLK in patient-derived GBM cells transduced with Mock control or NLK-WT vector. B. Comparison on the effects of NLK on in vitro proliferation. (+SD, n = 5) C. Limiting dilution assays (LDA) for in vitro tumor sphere formation. LDA clonogenic significance is measured by the linear regression analysis. D. Overexpression of NLK suppresses tumor sphere formation. Scale bar, 100 μm. E. Immunoblots of Sox2 and Nanog in NLK-WT or mock transduced GBM cells. F. Real-time RT-PCR analysis to determine the effects of NLK on mRNA expression levels of Sox2 and Nanog. G. Representative confocal images of immunofluorescence (IF) staining of Sox2 in spheroids. Scale bar, 100 μm. H. Immunoblots of anti-Flag and NLK in patient-derived GBM cells transduced with Mock control, NLK-WT or NLK Kinase-Negative (K/N) mutant vector. I. Comparison on the effects of NLK-WT and NLK K/N on in vitro proliferation. J. Limiting dilution assays (LDA) for in vitro tumor sphere formation.
