Figure 3. DCLK1 overexpression correlates with the activation of S100A9-NFκB inflammatory pathway in a hepatoma mouse xenografts model.
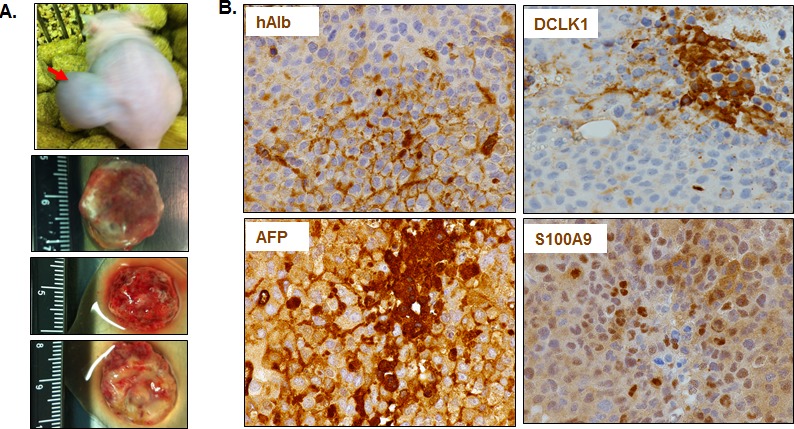
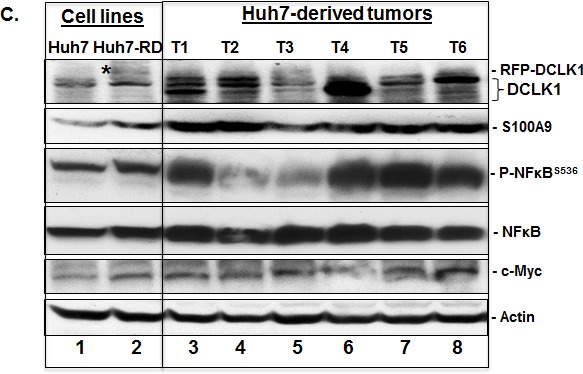
A. An example of Huh7 hepatoma cells-derived tumor within the flank of a nude athymic mouse. Three representative excised tumors from other mice are also shown. B. Representative results showing immunohistochemical staining of the tumors for human albumin (hAlb), DCLK1, α-fetoprotein (AFP) and S100A9. C. DCLK1 overexpression correlates with enhanced S100A9 expression, activation of inflammatory pathway indicated by extensive S536 phosphorylation of NFκB, and increase in c-Myc levels in the Huh7-derived tumors. One million Huh7 cells were transplanted into the flanks of nude/SCID mice. Western blot was carried out in total lysates prepared from six Huh7-derived tumors (T1 through T6, lanes 3-8). The levels were compared with the corresponding protein expression levels in the parent Huh7 cell lysates (lane 1) and Huh7-overexpressing human RFP-DCLK1 (Huh-RD, lane 2). Protein band indicated with a star in lane 2 represents recombinant RFP-DCLK1.
