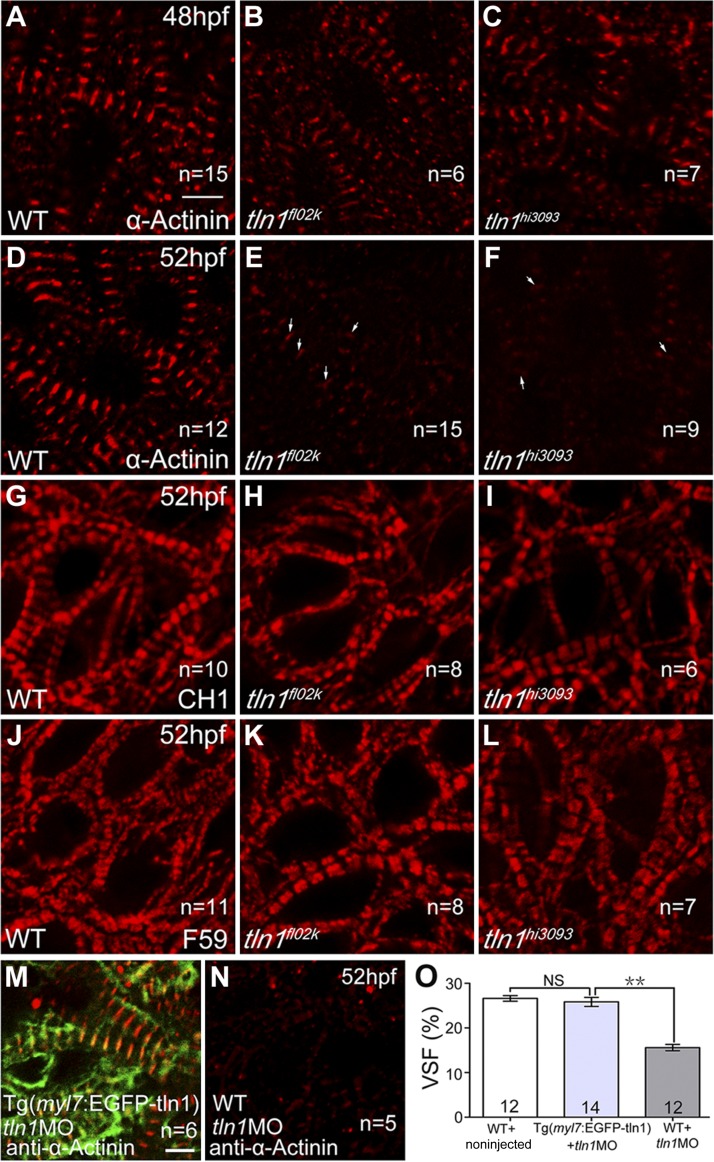
Figure 4.
Tln1 is critical for the stabilization of sarcomeric structures during heart development. Confocal images from the ventricles at 48 (A–C) and 52 (D–L) hpf with the indicated genotypes and antibody staining. The Z-disk staining by α-actinin was normal in tln1 mutants (B, C) compared with WT controls (A) at 48 hpf, but was disrupted in tln1 mutants (E, F) compared with WT controls (D) at 52 hpf; arrows pointed to a few weak Z-disks in mutants. The thin filament staining by CH1 was slightly affected in tln1 mutants (H, I) compared with WT controls (G) at 52 hpf, whereas the thick filament staining by F59 was comparable in WT (J) and tln1 mutants (K, L) at 52 hpf. M and N) The Z-disks in ventricular CMs, stained by anti–α-actinin, were rescued in tln1 morphants with the Tg(myl7:EGFP-tln1) transgene (M) compared with their nontransgenic siblings (N). n, hearts per group. O) VSF decreased in tln1 morphants (tln1-MO) compared with untreated WT controls, which was fully rescued in tln1 morphants by overexpression of the fusion gene EGFP-tln1 in CMs. **P < 0.01; number of hearts assayed is shown in the histograms. Scale bars, 4 μm (A–N).