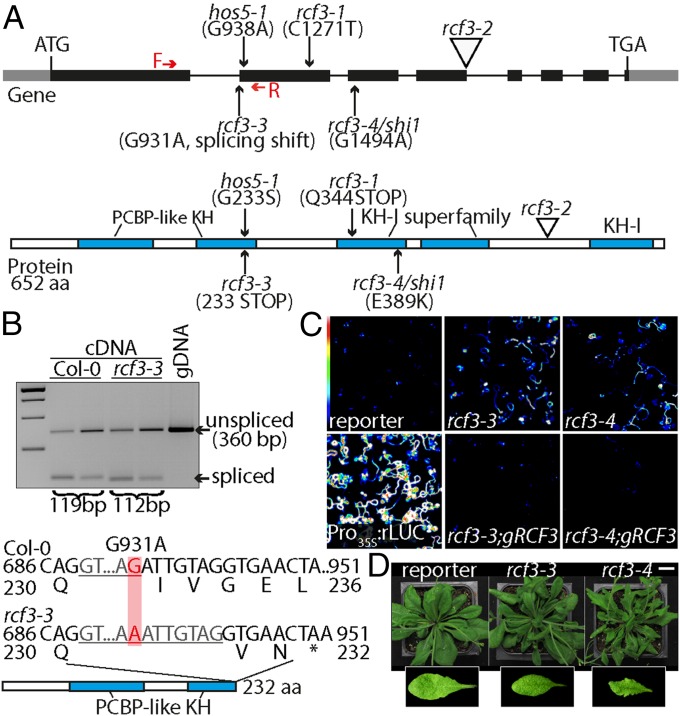
Fig. 1.
Characterization of rcf3 mutants. (A) Location and effects of mutations on the RCF3 protein. Red arrows note the forward and reverse primers used in B to detect the effect of rcf3-3 mutation on splicing. The five KH domains are marked in blue. (B) RT-PCR analysis of rcf3-3, with genomic DNA (gDNA) for comparison. Sequencing revealed use of a cryptic splice acceptor site in the mutant, leading to a frame shift containing an early stop codon. (C) Bioluminescence phenotype of rcf3 mutants, complemented mutants, amiRNA-activity reporter line (reporter), and Pro35S:rLUC controls. Colored scale indicates low (blue) to high (white) luminescence. (D) Morphological defects in rcf3 mutants. (Scale bar: 2 cm.)