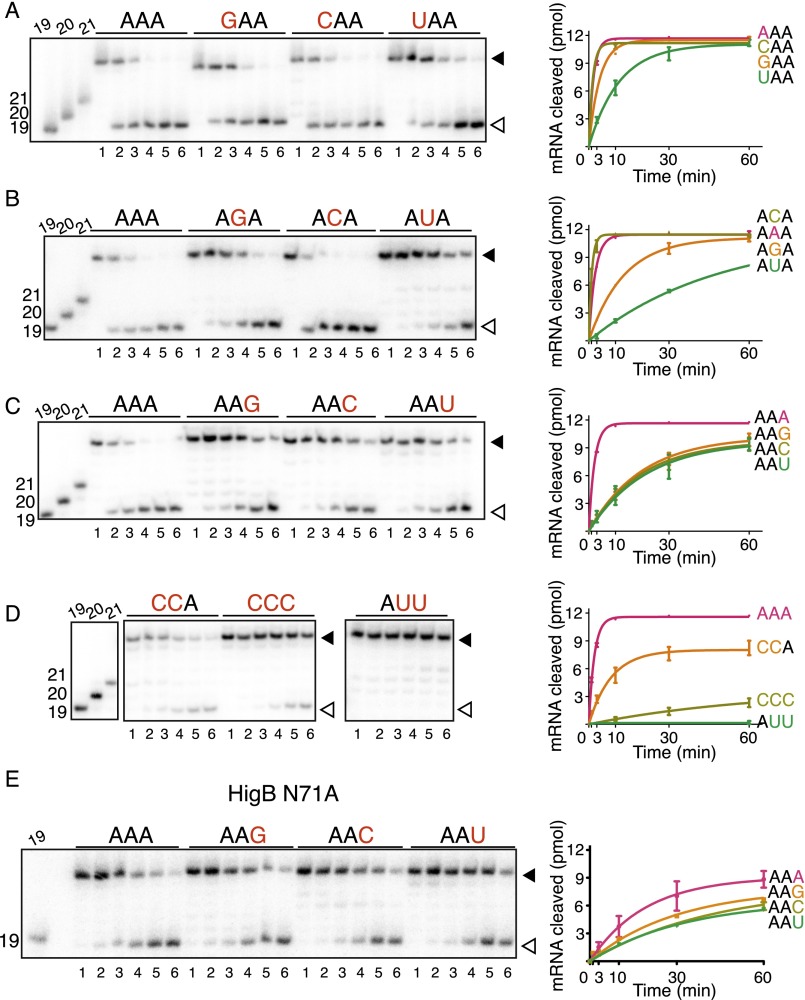
Fig. S5.
In vitro analyses of ribosome-dependent mRNA cleavage by HigB. E. coli 70S ribosomes were programmed with 5′-[32P]mRNA containing an A-site AAA lysine codon, P-site tRNAfMet, and HigB. The reaction was followed for 60 min, and the amount of mRNA cleaved (open arrow) compared with uncleaved (closed arrow) was determined by denaturing RNA gels (Left); 19-, 20-, and 21-mer standards are shown at the left of each gel. For wild-type HigB experiments, A-site mRNA was varied at the +4 nucleotide A-site position (A), the +5 nucleotide A-site position (B), the +6 nucleotide A-site position (C), and +4, +5 and +6 combinations (D). Lanes 1–6 represent 0, 1, 3, 10, 30, and 60 min time points for each codon tested in A–D. (E) For the HigB N71A variant, the +6 nucleotide A-site position was varied. Lanes 1–6 represent 1, 3, 10, 30, 60, and 120 min time points. The results were quantified using Image Quant, and product progression curves of the RNA gels are plotted on the (mean values ± SEM are displayed from at least two replicates) (Right).