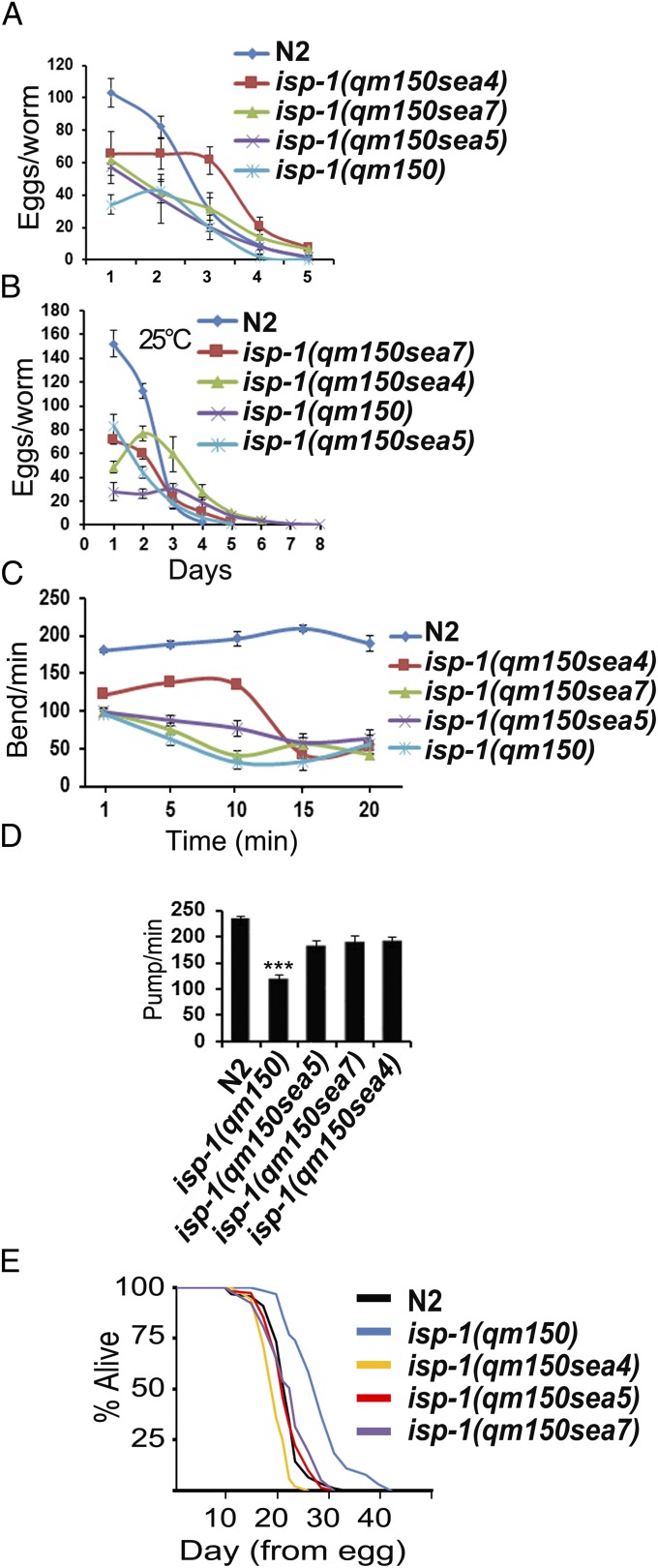
Fig. 2.
Physiological parameters of the isp-1(qm150) suppressors. (A and B) Brood size of N2, isp-1(qm150), and one of the suppressors at two different temperatures (20 °C and 25 °C), n = 25 for each strain/condition. (C) Thrashing in the course of 20 min. (D) Pharyngeal pumping rates, n = 30 per strain, the two-tailed heteroscedastic t test was performed on two strains at a time in all 10 combinations to establish which differences in pumping rate were statistically significant. (E) Lifespan of the suppressors, at 25 °C. The depicted result is a single typical trial. N2 (n = 90) isp-1(qm150) (n = 65), isp-1(qm150sea4) (n = 53), isp-1(qm150sea5) (n = 158), isp-1(qm150sea7) (n = 198). The graph indicates animals that died during the course of the experiment. Animals that left the agar surface are not considered. No other censoring was performed. Error bars: SEM for highlighted experiments, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.