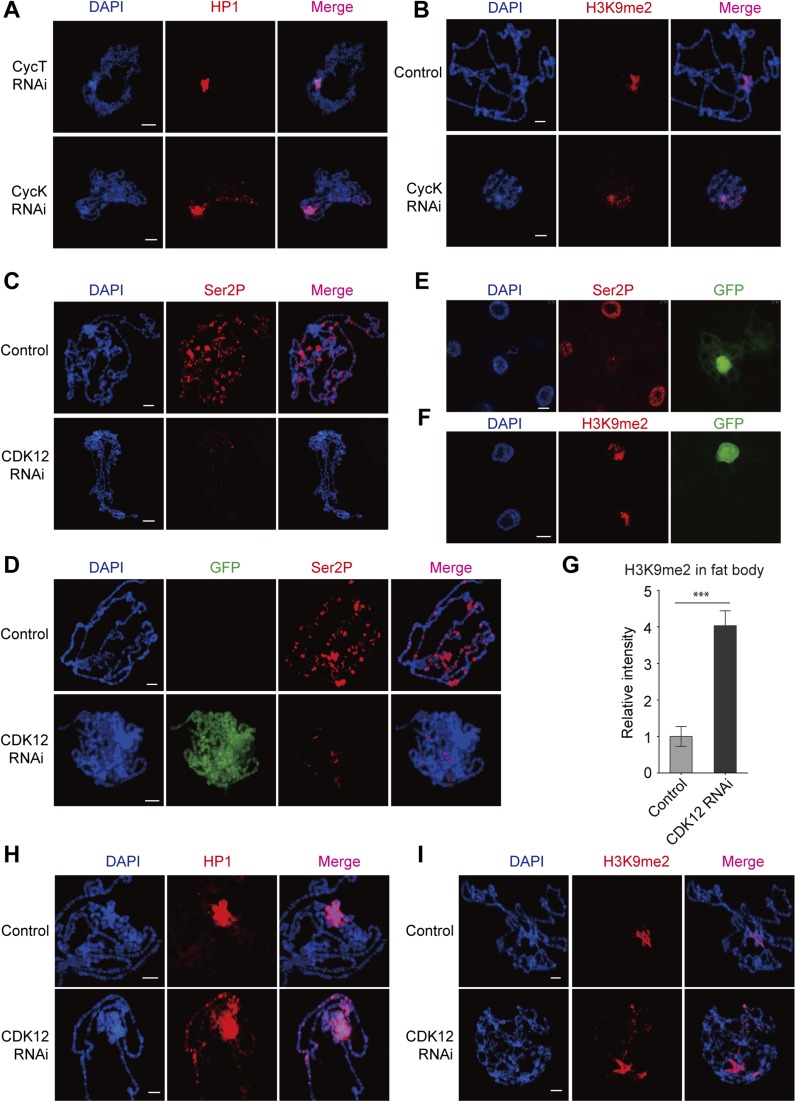
Fig. S2.
Depletion of CDK12/CycK induces heterochromatin ectopic accumulation. (A) Polytene chromosomes from CycK-depleted and CycT-depleted third-instar larvae were squashed and stained with anti-HP1 (C1A9; red). RNAi-induced knockdown was driven by SG-GAL4. (B) Chromosomes isolated from control and CycK-depleted larvae were stained with anti-H3K9me2 (red). (C) Ser2P was strongly decreased after CDK12 knockdown. Immunolocalization of Ser2P in polytene chromosomes isolated from WT control and CDK12-depleted larvae driven by SG-GAL4. (D–G) Ser2P was strongly decreased after CDK12 knockdown in clonal assay. (D) The polytene chromosome and (E and F) the fat body were dissected from third-instar larvae driven by the flip-out system and stained with Ser2P (red) in D and E and anti-H3K9me2 (red) in F. CDK12-depleted cells were detected by an antibody recognizing GFP, and cells without GFP staining served as a control. The relative fluorescence intensity of H3K9me2 on the euchromatic arms in the fat body cell is shown in G. Error bars indicate SD (n = 3). ***P < 0.001. (H and I) Heterochromatin enrichment occurs on euchromatic arms after CDK12 knockdown in the GAL80 system. The ectopic accumulations of (H) HP1 and (I) H3K9me2 on polytene chromosomes are shown. (Scale bar: 10 μm.)