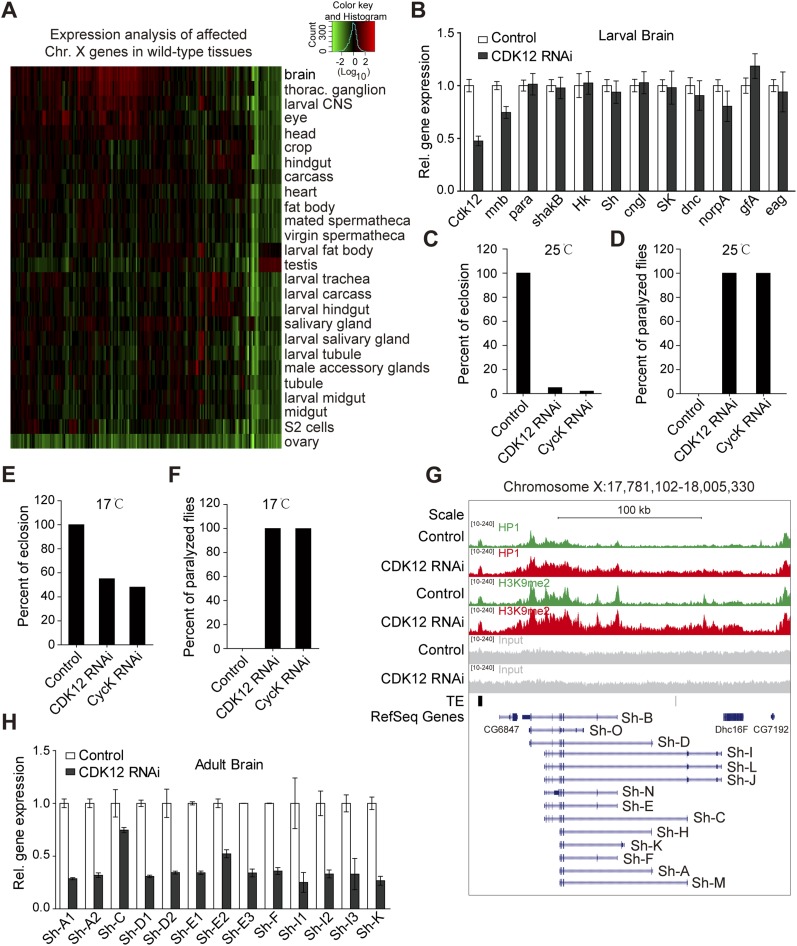
Fig. S5.
CDK12 does not affect neuronal gene expression in larval stage, and depletion of CDK12 induces locomotion defect in adult stage. (A) Heat map shows that the affected X-chromosome genes are highly expressed in the brain of WT Drosophila; 141 X-chromosome genes with increased H3K9me2 binding after CDK12 depletion are selected. Expression data in different tissues (mainly from the larval and adult stages) were obtained from the FlyAtlas database. The relative expression levels were determined using a log10 scale and normalized to the whole-fly genome-wide average. (B) The relative expression level of neuronal genes in third-instar larval brain after CDK12 depletion was monitored by qRT-PCR and normalized to rp49 mRNA; mnb showed no association with HP1 or H3K9me2 in our ChIP-seq analysis and served as a negative control. Error bars indicate SD (n = 3). (C) The percentage of eclosion from puparia was calculated in control, CDK12-depleted, and CycK-depleted flies. The CDK12 or CycK knockdown in the adult brain was driven by elav-GAL4 at 25 °C. (D) The percentage of flies showing paralyzed phenotype was calculated after CDK12 or CycK depletion. The CDK12 or CycK knockdown in the adult brain was driven by elav-GAL4 at 25 °C. (E) The percentage of eclosion from puparia was calculated as in C. The CDK12 or CycK knockdown in the adult brain was driven by elav-GAL4 at 17 °C. (F) The percentage of flies showing paralyzed phenotype was calculated as in D. The CDK12 or CycK knockdown in the adult brain was driven by elav-GAL4 at 17 °C. (G) The distribution pattern of HP1 and H3K9me2 within the Sh gene in CDK12-depleted (red) larvae and controls (green) is shown. Input (gray), transposable element (TE) locations (black), and reference genes (blue) are indicated. The isoforms of the Sh gene are shown at the bottom. The direction of transcription of the Sh gene is from right to left. (H) The relative expression levels of transcripts encoding different Sh isoforms were analyzed by qRT-PCR and normalized to rp49 mRNA. Primers were designed to target these isoforms, and some primers mapped more than one isoform of Sh. Error bars indicate SD (n = 3).