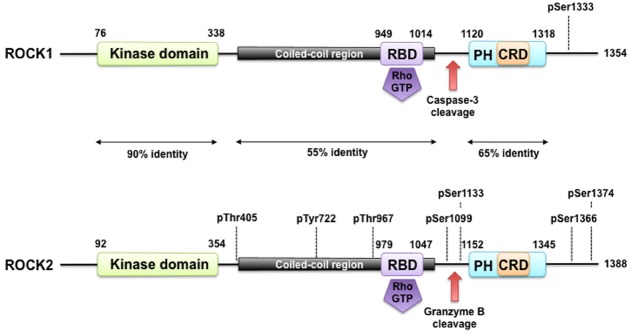
FIGURE 1.
ROCK structure and modes of regulation. ROCK1 and ROCK2 consist of an N-terminally located kinase domain and a C-terminally located pleckstrin homology (PH) domain containing a cysteine-rich C1 domain (CRD). The region between the ROCK kinase domain and the PH domain forms a coiled coil structure, in which the Rho binding domain (RBD) is located. Both are highly homologous and share overall 64% amino acid sequence identity. A splice variant of ROCK2 contains an insertion of 57 amino acids following the RBD and is called ROCK2m. ROCK1 and ROCK2 can be activated by binding of RhoGTP to the RBD and through cleavage of ROCK1 by caspase-3 and of ROCK2 by granzyme B and caspase-2. Autophosphorylation of ROCK1 at Ser1333 and of ROCK2 at Ser1366 reflects the activation status of the kinases. Phosphorylation of ROCK2 at Thr967, Ser1099, Ser1133, or Ser1374 increased its activation status, whereas phosphorylation of Tyr722 decreases the ability of ROCK2 to bind to RhoA. Interaction of Thr405 of ROCK2 with the N-terminal extension of the ROCK2’s kinase domain is essential for substrate phosphorylation and kinase domain dimerization.