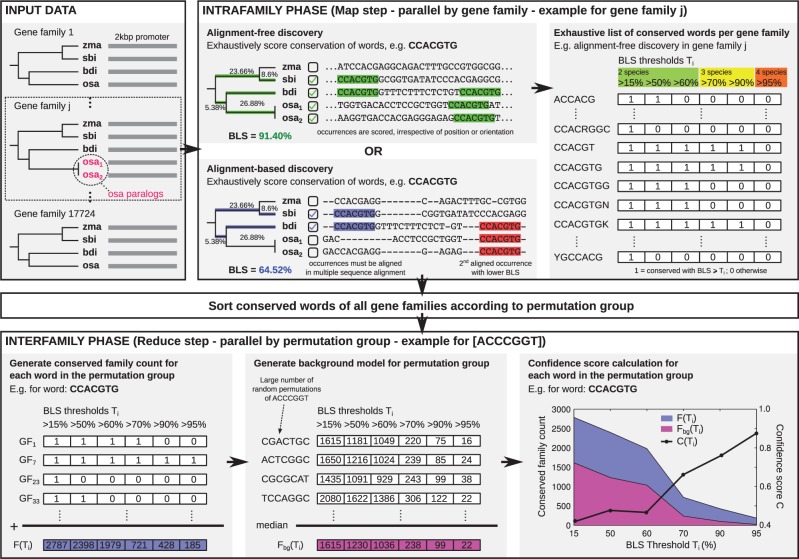
Fig. 1.
Overview of BLSSpeller. The input consists of homologous promoter sequences grouped into gene families. During the intrafamily phase, conserved words are exhaustively enumerated for each gene family individually. A word is considered to be conserved in a gene family if its branch length score (BLS) exceeds threshold T. Multiple BLS thresholds Ti can be used in a single run. In the alignment-free mode, the BLS of a word is computed irrespective of its orientation or relative position within the promoter sequences. Alternatively, in the alignment-based mode, words must appear aligned in the multiple sequence alignment. During the sorting phase, conserved words of all gene families are sorted according to permutation group, i.e. words with the same length and base content are grouped together. In the interfamily phase, permutation groups are handled individually. First, for each word, the conserved family count , i.e. the number of gene families in which the word is conserved with BLS , is established for all BLS thresholds Ti. Next, a background model is created by selecting the median value of the conserved family count of a large number of randomly generated instances of the permutation group, again for each threshold Ti. Finally, a confidence score is computed for each Ti. Words for which and for any threshold Ti are considered to be genome-wide conserved motifs and are retained