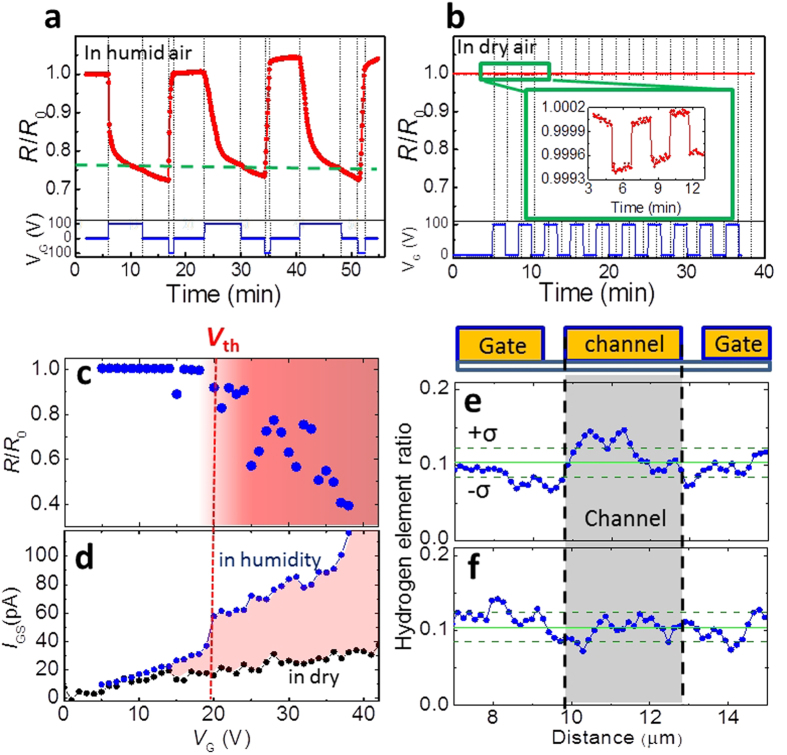
Figure 2. Effect of the electric field on the transport properties and hydrogen intercalations in a VO2 channel.
(a,b) Time dependence of the normalized resistance
(R/R0, where R0 is the
pristine resistance of a non-treated VO2 channel at
300 K with applied VG values of 100, 0 and
−100 V) (a) in humid air and (b) in
dry air. The green dashed line in (a) indicates the rough saturation
of R/R0. The inset in (b) is a magnified
view. (c) VG dependence of
R/R0 after applying a VG for
20 minutes. (d) VG dependence of the
current between the gate and source electrodes (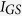 ) under a humidity of 60% (blue dotted-line) and in dry air (black
line). (e,f) The relative elemental ratios for hydrogen
normalized by oxygen (e) in a device after applying
VG = 100 V and
(f) in a pristine device. The solid and dashed green lines
represent the averages of the hydrogen atom profiles and the standard
deviations, respectively.
) under a humidity of 60% (blue dotted-line) and in dry air (black
line). (e,f) The relative elemental ratios for hydrogen
normalized by oxygen (e) in a device after applying
VG = 100 V and
(f) in a pristine device. The solid and dashed green lines
represent the averages of the hydrogen atom profiles and the standard
deviations, respectively.