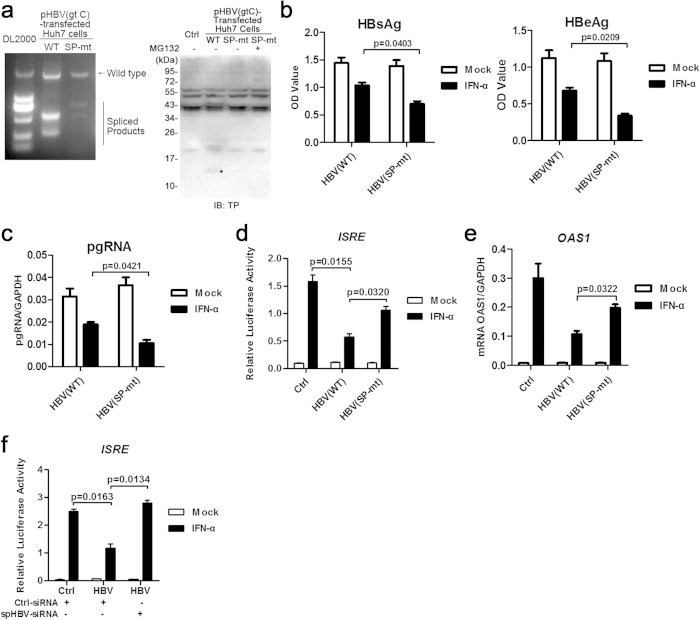
Figure 6. Mutation of the common splice sites of HBV impaired its anti-IFN activities in Huh7 cells.
The cDNAs reverse-transcripted from the total RNAs extracted from pHBV1.3- or pHBV1.3-SP-mt-transfected Huh7 cells were analyzed by PCR followed by agarose gel electrophoresis (a, the left panel). The expression of proteins in Huh7 cells transfected with indicated plasmids was analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-TP antibodies (a, the right panel). The level of HBsAg and HBeAg in culture supernatants 48 h post transfection was analyzed by ELISA (b). Huh7 cells were transfected with pHBV or pHBV(SP-mt) plasmids. IFN-α was added to the culture medium 24 h post transfection. Following an additional 24 h of culture, the RNAs were extracted for real-time PCR (c). Huh7 cells transfected with the indicated plasmids were mock- or IFN-α–treated for 12 h and then harvested for luciferase reporter assay (d), or for 6 h and then RNAs were extracted for real-time PCR (e). Huh7 cells co-transfected with pHBV and control siRNAs or siRNAs targeting spHBV RNAs were mock- or IFN-α–treated for 12 h and then harvested for luciferase reporter assay (f). The data was analyzed using Student’s t-tests.