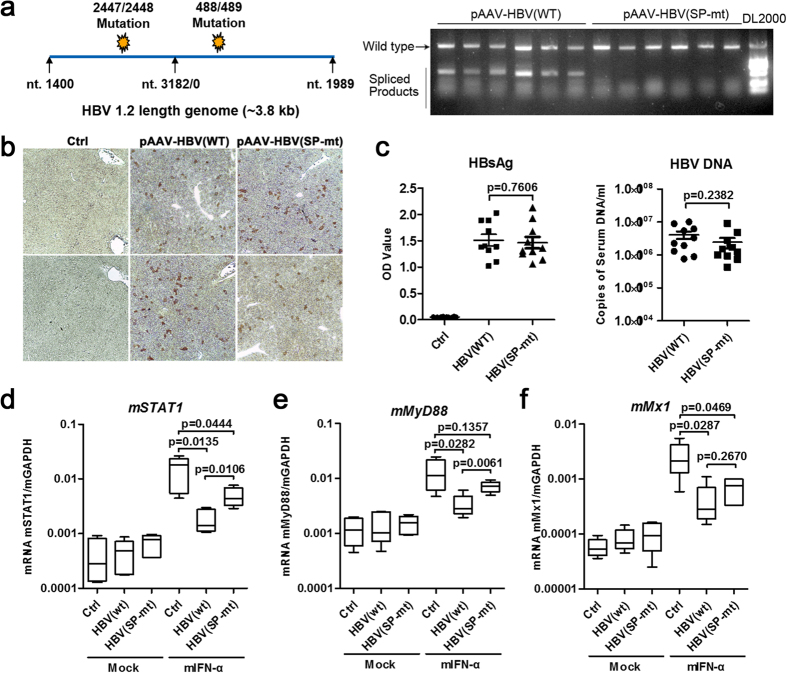
Figure 7. Mutagenesis analysis of the role of HBV splicing in viral anti-IFN effects in the hydrodynamic injection-based mouse model.
pAAV/HBV1.2(SP-mt) was constructed by introducing two mutations of the common spliced acceptor and donor sites of HBV genome into pAAV/HBV1.2 and the mutations resulted in an impaired generation of spliced RNAs (a). Immunohistochemical staining for HBcAg in hepatocytes of mice injected with control vectors or the pHBV(wt) and pHBV(SP-mt) plasmids (b). Serum levels of HBsAg and viral DNA of the mice injected with indicated plasmids (2 weeks post injection) were determined by ELISA and qPCR, respectively (c). Intrahepatic RNA levels of mSTAT1 (d), mMyD88 (e), and mMx1 (f) were analyzed 6 h after mIFN-α or saline treatment in 6 different experimental groups (n = 5 in each group). The data was analyzed by one-way analysis of variance followed by Bonferroni tests.