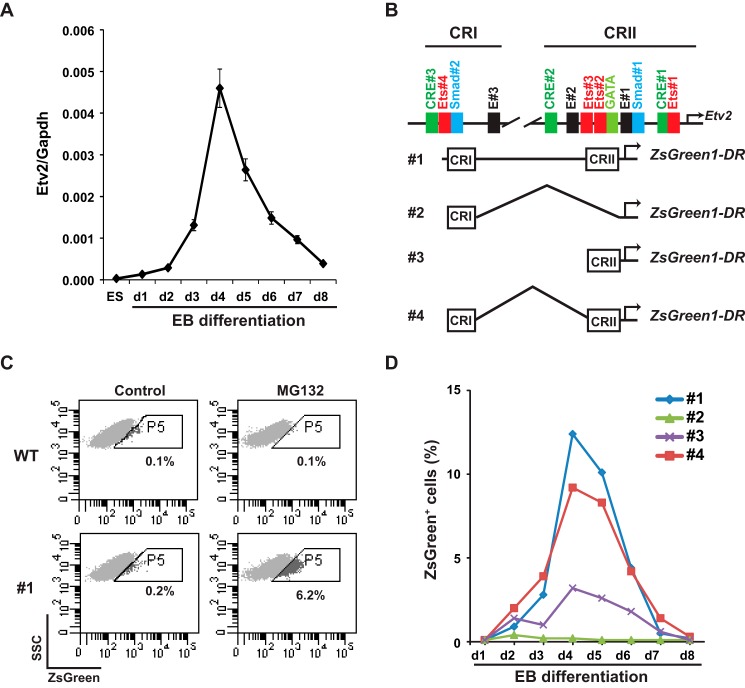
FIGURE 2.
Characterization of the Etv2 cis-regulatory module. A, gene expression of Etv2 during wild-type A2lox ES cell/EB differentiation. Note that Etv2 transcript expression is undetectable in the undifferentiated ES cells. B, schematic of the 3.9-kb Etv2 promoter-reporter constructs. Top panel, two conserved regions were identified in the 3.9-kb upstream fragment and include CRI and CRII. Note that motifs are designated in the CRI and CRII region. Bottom panel, schematic of the ZsGreen1-DR reporters fused with the 3.9-kb Etv2 promoter, CRI, CRII, and CRI+CRII. C, FACS profile of side scatter (SSC) versus ZsGreen in A2lox ES harboring the ZsGreen1-DR reporters during EB differentiation. MG132 treatment has no effect on the WT A2lox ES cells but increases the ZsGreen signal in ES cell #1 upon embryonic differentiation from 0.2% to 6.2%. Controls were treated with DMSO because MG132 was dissolved in DMSO. WT, A2lox ES cells; #1, A2lox ES cells harboring the 3.9-kb fragment linked to the ZsGreen1-DR construct. D, FACS profiles of ES cells harboring constructs #1, #2, #3, and #4 during EB differentiation. Note the similar patterns between the Etv2 gene expression in A and the FACS profile of ES cell line #1. Compared with the profile of ES cell line #1, the ZsGreen+ cells of the ES cell line #3 are reduced. The signal in ES cell line #2 is minimal, whereas that in ES cell line #4 is almost the same as that in ES cell line #1.