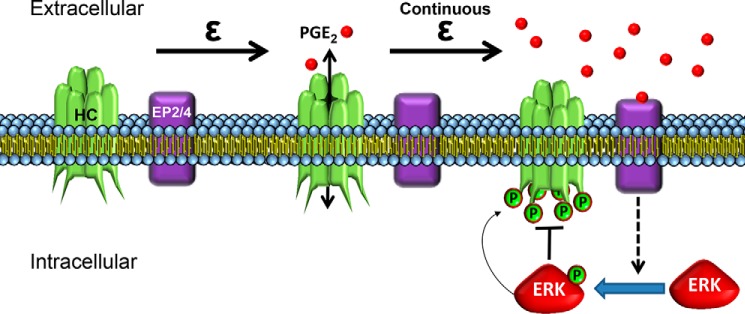
FIGURE 7.
A schematic model showing the hemichannel closure after long FFSS is regulated by Cx43 phosphorylation by MAPK, which is activated by extracellular PGE2 released by hemichannels via feedback inhibition mechanism. During short term FFSS, Cx43 hemichannels (HC) in osteocytes are induced open, which allows the release of bone modulating factors such as PGE2. A sustained mechanical stimulation causes Cx43 hemichannel closure due to accumulation of PGE2 in the extracellular environment. The accumulated PGE2, likely through the EP2/EP4 receptor, activates p44/42 MAPK and increases Cx43 phosphorylation at Ser279-Ser282 residues thereby leading to closure of Cx43 hemichannels.