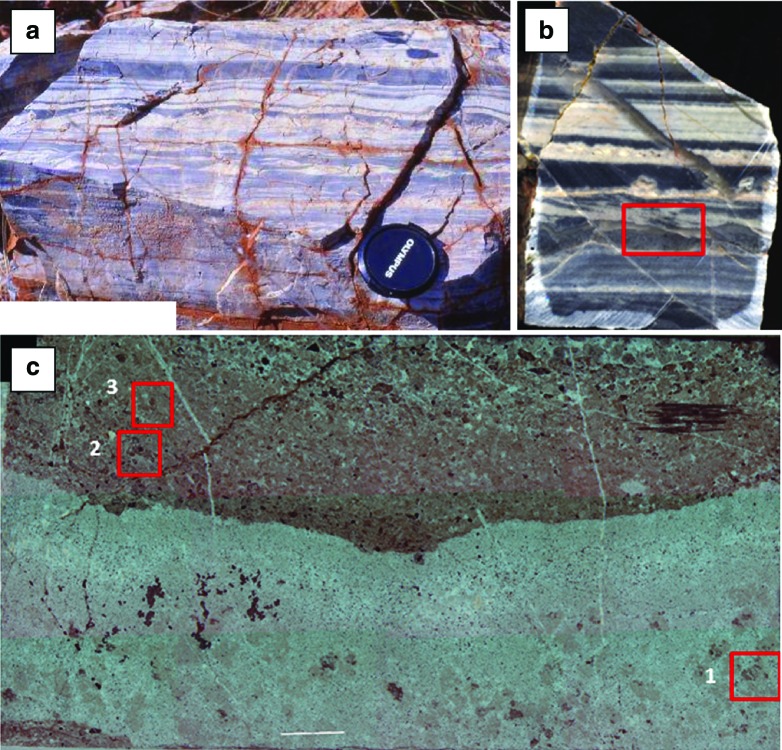
FIG. 10.
Kitty's Gap Chert (3.45 Ga), Pilbara, Australia. (a) Field view showing finely layered, volcanic sediments (silicified) exhibiting sedimentary structures including flaser bedding (lenticular-shaped layers), cross bedding (inclined laminations), and suspension settling (parallel laminae). Note the coarser, blocky grains (pumice) at the top of some of the layers. The lens cap is 6.8 cm in diameter. (b) Details of the sedimentary structures showing parallel and cross bedding. The red box marks the details shown in (c). (c) Micrograph of a thin section viewed in transmitted light. The lower, clear part represents an intrusive hydrothermal chert vein that penetrated into the already slightly lithified sediment. The upper part shows inclined, normally graded beds of fine to medium sand at the base grading upward into finer (silt to clay), poorly sorted sediments. The red boxes mark details documented by μ-Raman spectral mapping illustrated in Fig. 11. (Color graphics available at www.liebertonline.com/ast)