Fig. 6.
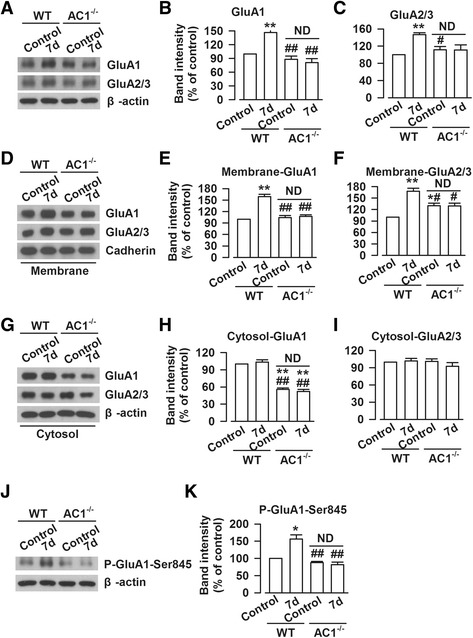
Genetic deletion of AC1 reduced the increased expression of AMPA receptor. a Representative Western blot for GluA1 and GluA2/3 in the ACC obtained from WT or AC1−/− control and zymosan-injected mice. b-c The enhanced expressions of GluA1 (b) and GluA2/3 (c) were reduced in the ACC of AC1−/− mice on day 7 after zymosan treatment. d Representative Western blot for membranous proteins of GluA1 and GluA2/3 in the ACC obtained from WT or AC1−/− control and zymosan-injected mice. e-f The enhanced membranous expressions of GluA1 (e) and GluA2/3 (f) were completely or partly blocked in the ACC of AC1−/− mice on day 7 after zymosan treatment. g Representative Western blot for cytoplasmic proteins of GluA1 and GluA2/3 in the ACC obtained from WT or AC1−/− control and zymosan-injected mice. h The cytoplasmic protein of GluA1 was significantly decreased in the ACC of AC1−/− mice as compared with that in WT mice. i There was no difference on cytoplasmic protein of GluA2/3 among four groups. j Representative Western blot for phosphorylated GluA1 at the Ser845 site in the ACC obtained from WT or AC1−/− control and zymosan-injected mice. k The increased phosphorylation of GluA1 at the Ser845 site was significantly inhibited in the ACC of AC1−/− mice on day 7 after zymosan treatment. N = 6 mice per group, * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01 vs. WT control; # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01 vs. WT for 7d
