Fig. 6.
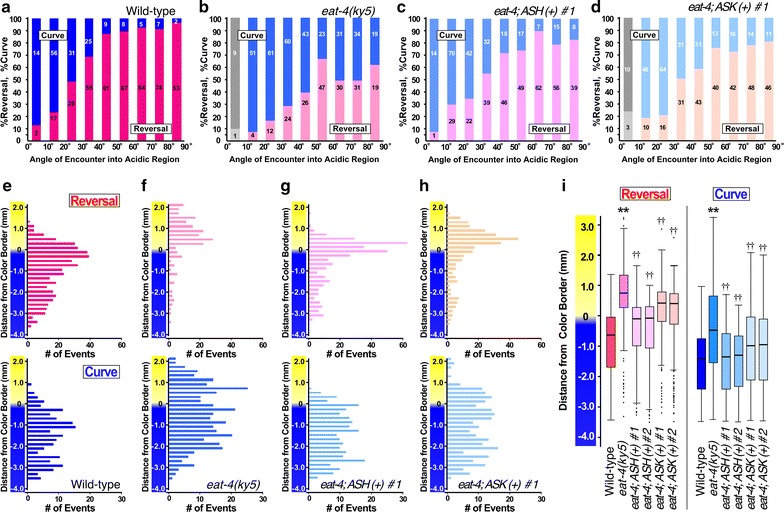
Acidic pH avoidance behavior of the eat-4(ky5) mutant. a–d Ratio of the behavioral choice, e-h histogram of distance and i boxplot of the distance distributions. Experiments were performed under the same conditions as in Fig. 2. Wild-type (a, e), eat-4(ky5) (b, f), eat-4(ky5); ASH::eat-4(wt) strain [ASH(+); c, g]. eat-4(ky5); ASK::eat-4(wt) [ASK(+); d, h] were examined. ASH (+) and ASK(+) are transgenic strains harboring a transgene driving ASH- and ASK-specific expression of the wild-type eat-4 gene, respectively. The ratio of reversal had a positive correlation with the angle in all strains (R > 0.9, p < 0.01). In (i), statistical differences were examined using Student’s t test. Asterisk indicates a significant difference between wild-type and eat-4(ky5) (**p < 0.01). Dagger indicates a significant difference between the eat-4(ky5) and ASH(+), ASK(+) strain (†† p < 0.01)
