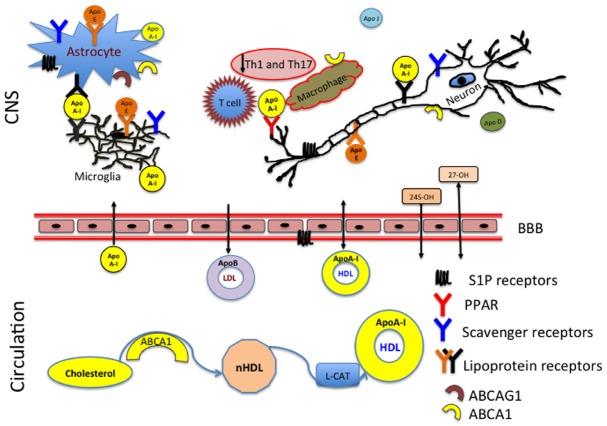
FIGURE 1.
ApoA-I reduces inflammation in the CNS by preventing contact between the T cells and macrophages. HDL produced in the periphery has access to the CNS whereas LDL has no ability to enter the CNS from the circulation. The membrane associated ATP-binding cassette subfamily A member 1 (ABCA1) and ABCA G1 act as the primary sterol transporters for ApoA-I/HDL. HDL associated ApoA-I is then recognized by the lipoprotein receptors (LDL, SR-BI) in the CNS. Brain cholesterol homeostasis is supported by the reverse cholesterol transport and efflux of 24 (24S-OH) and 27 (27-OH) hydroxysterols through the blood–brain barrier (BBB).