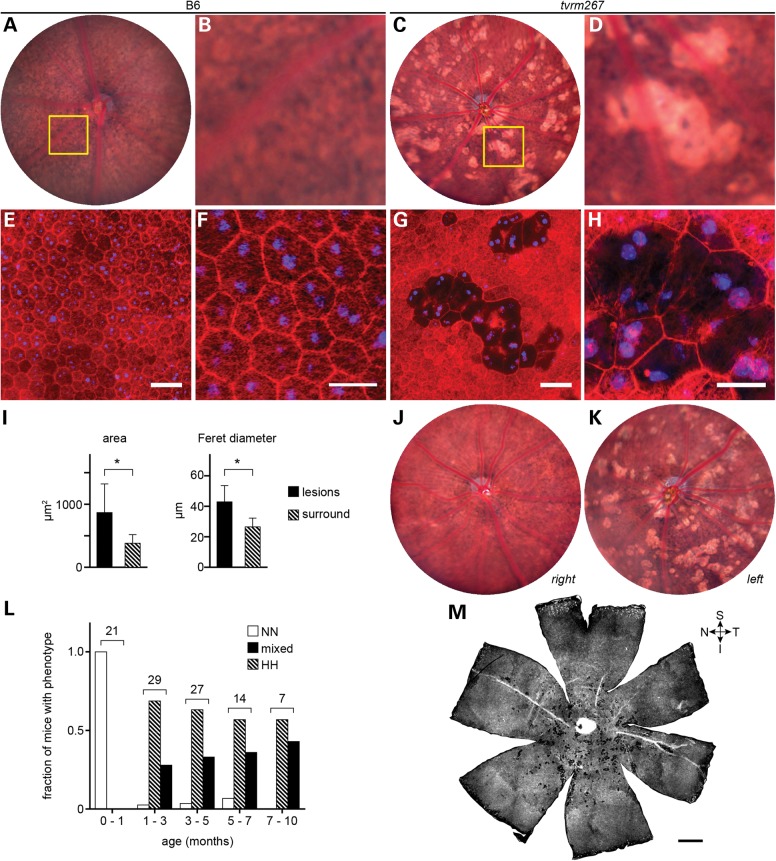
Figure 4.
Adamtsl4tvrm267 mice develop RPE lesions. (A) Bright field fundus image of a WT (B6) mouse at 3 months of age. (B) Detail of boxed area in (A) showing the normal appearance of the RPE. (C) Bright lesions, consistent with hypopigmentation, in a 3-month-old Adamtsl4tvrm267 mutant. (D) Detail of boxed area in (C) showing an alteration in pigmentation among RPE cells associated with bright lesions. (E–H) Fluorescence micrographs of RPE flatmounts stained for F-actin (rhodamine phalloidin, red) and nuclei (DAPI, blue). (E) WT flatmount showing the normal polygonal architecture of the RPE as revealed by F-actin staining at cell boundaries. (F) Detail of panel (E) showing mono- and binucleated cells, and phalloidin staining within cell boundaries due to F-actin in apical processes. (G) Flatmount of the homozygous Adamtsl4tvrm267 eye shown in panels (C) and (D) indicating a precise correspondence of the lesions. (H) Detail of panel (G) showing that in areas associated with lesions, many cells are enlarged and have diminished phalloidin staining (n = 3). (I) Morphometric analysis of Adamtsl4tvrm267 mice at 3 months of age indicating an increase in area and Feret diameter of RPE cells within lesions. Cells within lesions (n = 55) were compared with cells in the area surrounding the lesions (n = 372). Asterisks: P < 0.0001; error bars indicate mean ± SD. (J and K) Fundus images (J, right eye; K, left eye) showing the variability in lesion severity within an individual homozygous Adamtsl4tvrm267 mouse. (L) Incidence of RPE lesions with age. The splatter phenotype was graded in homozygous Adamtsl4tvrm267 eyes by indirect ophthalmoscopic evaluation (severity of phenotype: N, none; L, low; M, medium; H, high; see grading scale in Supplementary Material, Fig. S1). The number of mice with a grade in both eyes of no (NN) or high (HH), or any other combination (mixed) was determined in ranges up to ∼10 months of age. The total number of mice examined within each age range is indicated. Mice were free of lesions up to 1 month of age. The fraction with a mixed or bilateral high splatter phenotype increased dramatically between 1 and 3 months and progressed slowly thereafter. (M) Whole flatmount from a homozygous Adamtsl4tvrm267 eye showing a regional distribution of lesions in the mutant near the optic nerve head with a bias toward the inferior fundus. Quadrants are designated S, superior; I, inferior; T, temporal; N, nasal. B6 controls: (A, B, E and F); tvrm267 mutants: (C, D, G, H, J, K, M). Scale bars: (E and G) 50 µm; (F and H) 25 µm; (M) 500 µm.