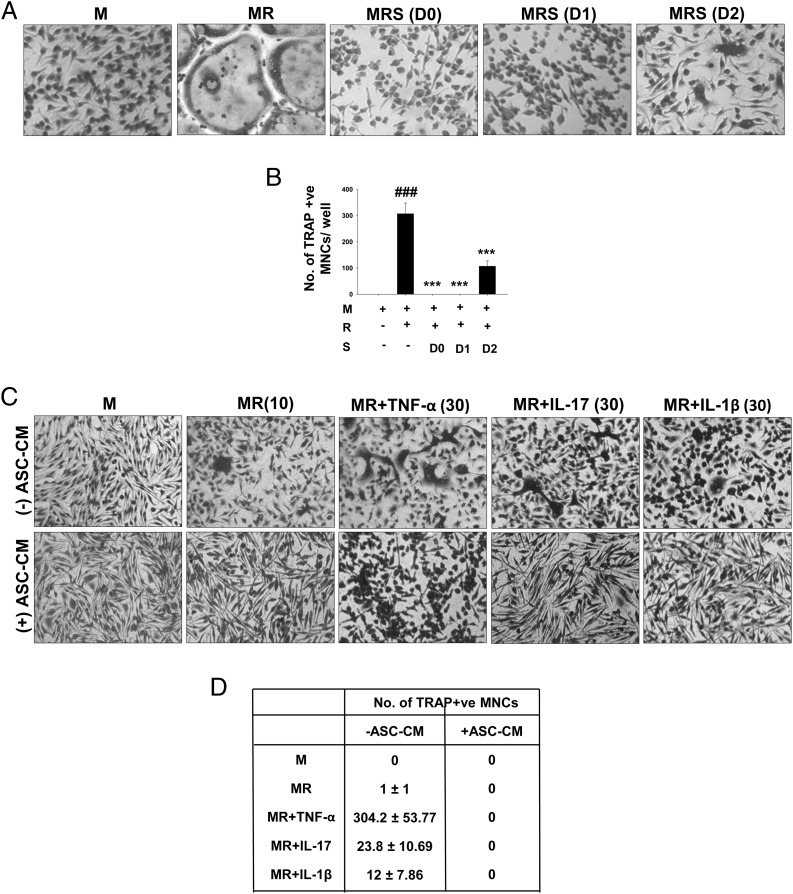
FIGURE 4.
ASC-CM potently inhibits osteoclastogenesis. M-CSF–dependent OCPs were differentiated into osteoclasts using M-CSF (30 ng/ml) and RANKL (40 ng/ml). ASC-CM was added at three different time points along the course of differentiation, that is, on days 0, 1, and 2. Cultures were fixed after 4 d and stained for TRAP. Representative images (A) and numbers (B) of osteoclasts in the cultures are shown (original magnification ×10). ###p ≤ 0.001 compared with M-CSF group; ***p ≤ 0.001 compared with M-CSF and RANKL group. (C and D) OCPs were cultured using M-CSF and RANKL (10 ng/ml) with or without proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-17, and IL-1β at a concentration of 30 ng/ml. ASC-CM was added to these cultures at 50% volume. Cultures were terminated after 3 d and stained for TRAP (original magnification ×10). Numbers are represented as mean ± SEM of five replicates in each group. Data are shown as representative images (C) and numbers of osteoclasts (D) of two independent experiments. M, M-CSF; MR, M-CSF and RANKL; MRS, M-CSF and RANKL with ASC-CM.