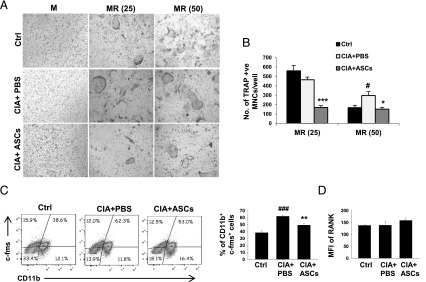
FIGURE 7.
ASCs decrease RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in CIA mice by reducing osteoclast precursors. CIA mice were injected i.p. with PBS or 2 × 106 ASCs on day 22 of the first immunization and sacrificed on day 36. Bone marrow was harvested and M-CSF–dependent OCPs were differentiated into osteoclasts in the presence of M-CSF with or without two different concentrations of RANKL (25 or 50 ng/ml). Representative images (A) and numbers of osteoclasts (B) in cultures are shown as a measure of osteoclastogenesis (original magnification ×10). (C) Percentage of osteoclast precursors (CD11b+c-fms+) in bone marrow. (D) The amount of RANK expressed on CD11b+ cells of bone marrow. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of seven mice per group in (B), four to five mice per group in (C), and five mice per group in (D). Significance was calculated by a one-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni multiple comparisons test between 1) control versus CIA plus PBS groups and 2) CIA plus PBS versus CIA plus ASC groups. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. #p ≤ 0.05, ###p ≤ 0.001 with respect to control group; *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001 with respect to CIA plus PBS group. M, M-CSF; MR, M-CSF and RANKL.